Details of Host Protein-DME Interaction (HOSPPI)
| General Information of Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME ID: DME0114) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DME Name | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 (COX-2), Homo sapiens | DME Info | |||
| UniProt ID | |||||
| EC Number | EC: 1.14.99.1 (Click to Show/Hide the Complete EC Tree) | ||||
| Lineage | Species: Homo sapiens (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage) | ||||
| Interactome | |||||
| Disease Specific Interactions between Host Protein and DME (HOSPPI) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification Healthy | |||||
| ICD-11: Healthy | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 16 HOSPPI | ||||
| Oligomerization | |||||
| Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2) | Health | Heterodimer | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | COX2-PTGS2 heterodimerization | [2] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Insect cell microsomes | ||||
| Affected Substrate(s): | Arachidonic acid (Metabolic product: Prostaglandin endoperoxide H(2)) | ||||
| Description | Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2) is reported to heterodimerize with the COX2 protein, which leads to an increased activity of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between COX2 and COX2 can facilitate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Transcription-factor regulation | |||||
| AMP element-binding 1 (CREB1) | Health | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | CREB1-PTGS2 interaction | [1] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Human amnion fibroblast cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | AMP element-binding 1 (CREB1) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between CREB1 and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Early growth response 1 (EGR1) | Health | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | EGR1-PTGS2 interaction | [3] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Human mammary and oral epithelial cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Early growth response 1 (EGR1) is reported to repress the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between EGR1 and COX2 can repress the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ETS translocation 4 (ETV4) | Health | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | ETV4-PTGS2 interaction | [4] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Mouse mammary epithelial cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | ETS translocation 4 (ETV4) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between ETV4 and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| His-acetyltransferase p300 (EP300) | Health | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | EP300-PTGS2 interaction | [5] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Human foreskin fibroblasts | ||||
| Description | His-acetyltransferase p300 (EP300) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between EP300 and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | Health | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | HDAC1-PTGS2 interaction | [6] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | BEAS-2B cell line | ||||
| Description | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) is reported to deacetylate the COX2 gene and thereby represses the transcriptional activity of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between HDAC1 and COX2 can inhibit the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Nuclear factor kappa-B p105 (NFKB1) | Health | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | NFKB1-PTGS2 interaction | [11], [12], [13] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Human bronchial epithelial primary cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Nuclear factor kappa-B p105 (NFKB1) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between NFKB1 and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Proto-oncogene c-Fos (FOS) | Health | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | FOS-PTGS2 interaction | [14] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Human chondrocytes | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Proto-oncogene c-Fos (FOS) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between FOS and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| SET-binding protein (SETBP1) | Health | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | SETBP1-PTGS2 interaction | [15] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Airway structural cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | SET-binding protein (SETBP1) is reported to repress the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between SETBP1 and COX2 can repress the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| TF factor jun-B (JUNB) | Health | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | JUNB-PTGS2 interaction | [14] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Human chondrocytes | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | TF factor jun-B (JUNB) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between JUNB and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| TF factor jun-D (JUND) | Health | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | JUND-PTGS2 interaction | [14] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Human chondrocytes | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | TF factor jun-D (JUND) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between JUND and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Transcription factor p65 (RELA) | Health | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | RELA-PTGS2 interaction | [11], [12], [13] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Human bronchial epithelial primary cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Transcription factor p65 (RELA) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between RELA and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Non-coding RNA regulation | |||||
| hsa-miR-146a-5p | Health | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-146a-5p--PTGS2 regulation | [8] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | GES-1 and HEK293 cell lines | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-146a-5p is reported to suppress PTGS2 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of PTGS2 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| hsa-miR-199a-5p | Health | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-199a-5p--PTGS2 regulation | [9] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | BEAS-2B cell line | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-199a-5p is reported to suppress PTGS2 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of PTGS2 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| hsa-miR-558 | Health | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-558--PTGS2 regulation | [10] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | SW1353 cell line | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-558 is reported to suppress PTGS2 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of PTGS2 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Histone modification | |||||
| Histone methyltransferases (HMTs) | Health | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | HMTs-COX2 interaction | [7] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Mouse embryonic fibroblast cells | ||||
| Description | The Histone 3 lysine 9 trimethylation of COX2 gene is reported to repress the transcriptional activity of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between Histone methyltransferases (HMTs) and COX2 can inhibit the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ICD Disease Classification 02 Neoplasms | |||||
| ICD-11: 2A00 Brain cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 6 HOSPPI | ||||
| Transcription-factor regulation | |||||
| Homeobox protein CDX-2 (CDX2) | Glioblastoma | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | CDX2-PTGS2 interaction | [16] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | U87 cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Homeobox protein CDX-2 (CDX2) is reported to repress the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between CDX2 and COX2 can repress the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| STAT 3 (STAT3) | Glioblastoma | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | STAT3-PTGS2 interaction | [19] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | U87MG and T98G cell lines | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | STAT 3 (STAT3) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between STAT3 and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Upstream stimulatory 1 (USF1) | Medulloblastoma | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | USF1-PTGS2 interaction | [20] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | TE671 cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Upstream stimulatory 1 (USF1) is reported to repress the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between USF1 and COX2 can repress the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Non-coding RNA regulation | |||||
| hsa-miR-137 | Glioblastoma | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-137--PTGS2 regulation | [17] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | LN229 cell line | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-137 is reported to suppress PTGS2 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of PTGS2 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| hsa-miR-26b-5p | Glioblastoma | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-26b-5p--PTGS2 regulation | [18] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | U373 cell line | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-26b-5p is reported to suppress PTGS2 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of PTGS2 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| DNA methylation | |||||
| DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) | Multilayered rosettes embryonal tumour | Significant hypermethylation | |||
| Interaction Name | DNMT-COX-2 interaction | ||||
| The Methylation Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | Significant hypermethylation p-value: 1.36E-20; delta-beta: 8.00E-01 | ||||
| Description | DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) is reported to significantly hyper-methylate the COX-2 gene, which leads to a significantly decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between DNMT and COX-2 can significantly affect the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
|
DME methylation in the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
|||||
| Violin Diagram of DME Disease-specific Methylation Level |
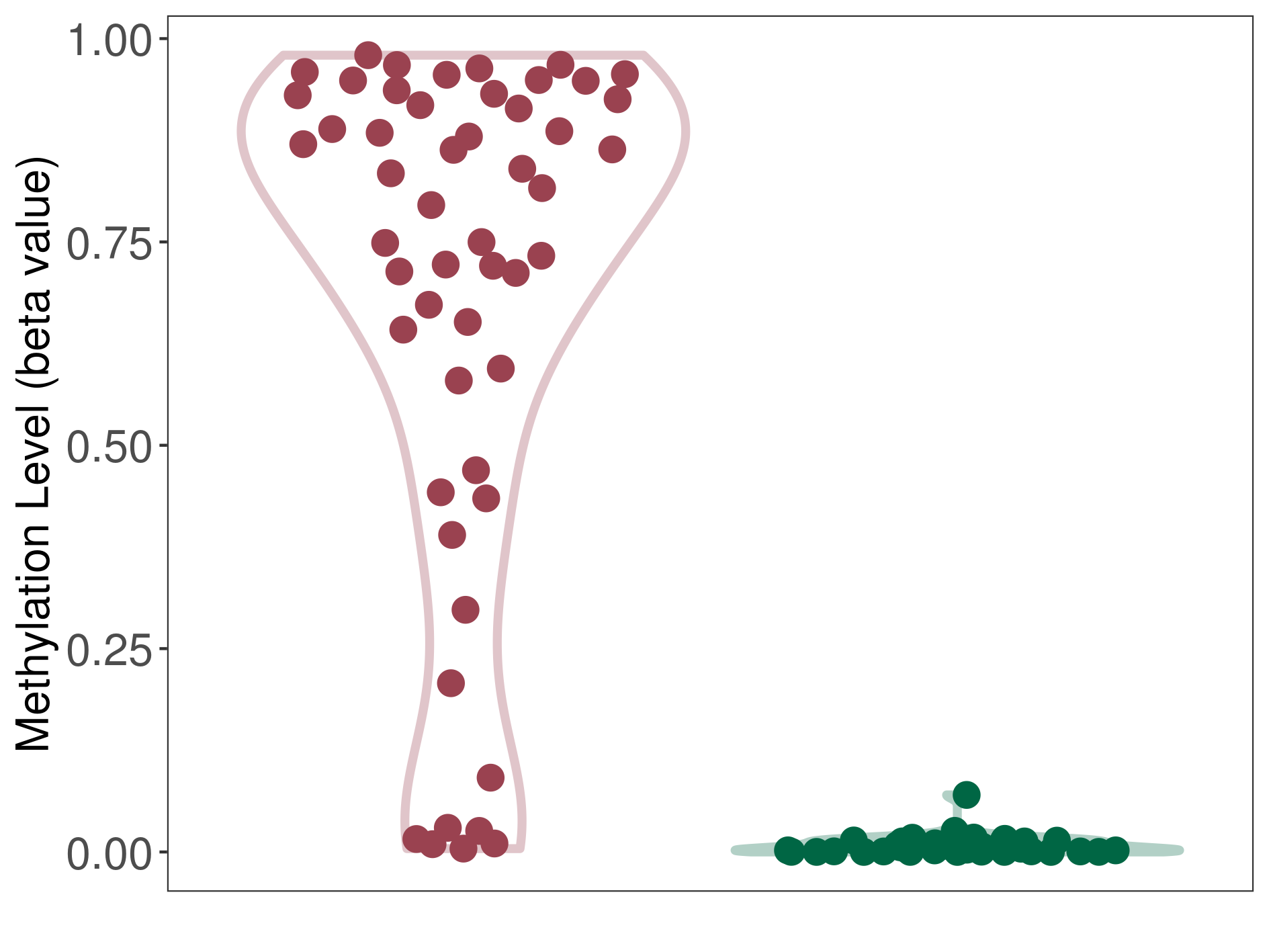
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram | |||
| ICD-11: 2B30 Lymphoma | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| DNA methylation | |||||
| DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) | Lymphoma | Significant hypermethylation | |||
| Interaction Name | DNMT-COX-2 interaction | ||||
| The Methylation Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | Significant hypermethylation p-value: 1.66E-17; delta-beta: 5.52E-01 | ||||
| Description | DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) is reported to significantly hyper-methylate the COX-2 gene, which leads to a significantly decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between DNMT and COX-2 can significantly affect the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
|
DME methylation in the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
|||||
| Violin Diagram of DME Disease-specific Methylation Level |
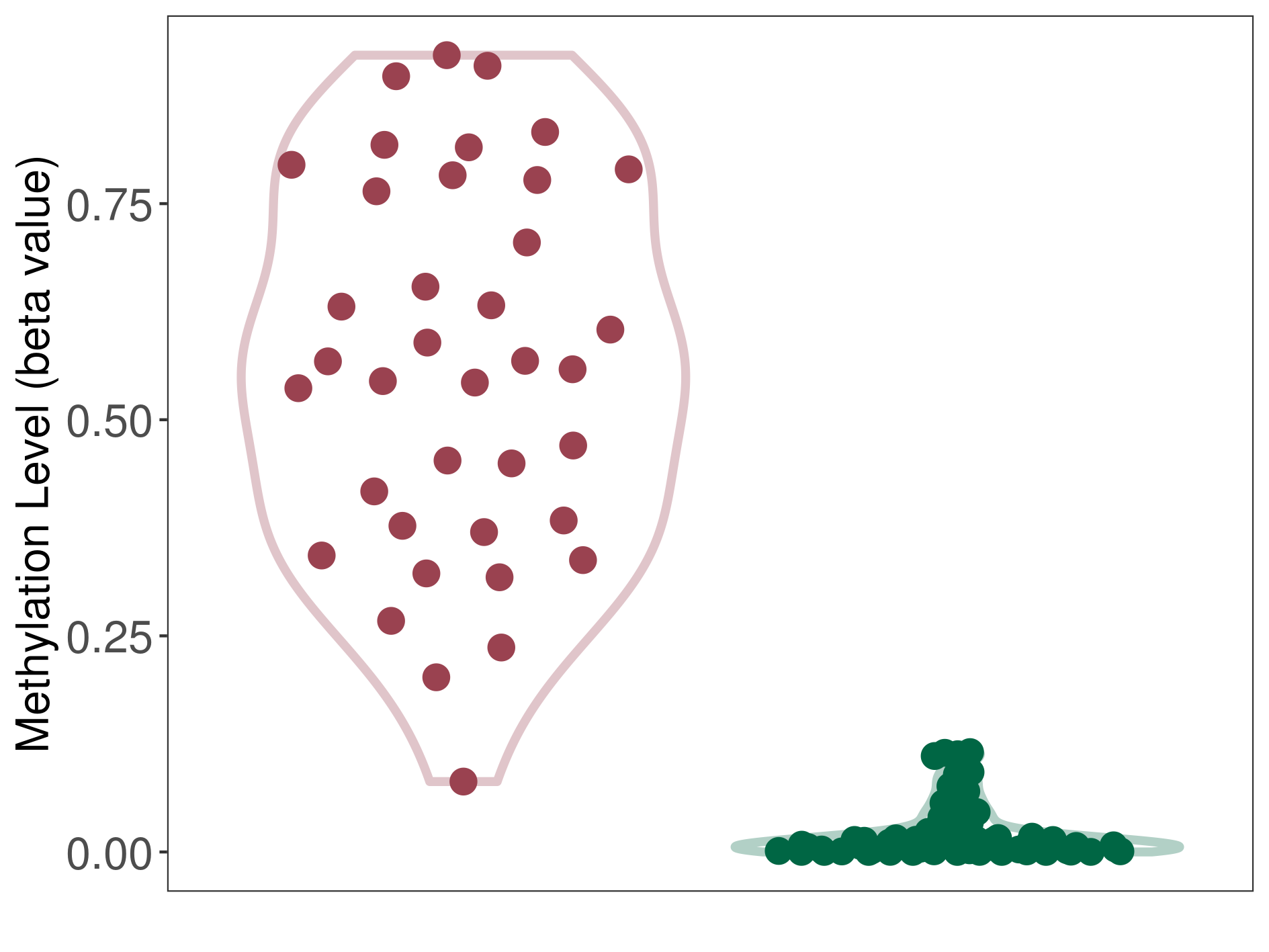
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram | |||
| ICD-11: 2B90 Colorectal cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 5 HOSPPI | ||||
| Transcription-factor regulation | |||||
| Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) | Colorectal cancer | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | APC-PTGS2 interaction | [21], [22] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | HT-29 cell line | ||||
| Description | Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) is reported to repress the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between APC and COX2 can repress the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Homeobox protein CDX-2 (CDX2) | Colorectal cancer | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | CDX2-PTGS2 interaction | [16] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | HCT-116 and SNU-C4 cell lines | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Homeobox protein CDX-2 (CDX2) is reported to repress the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between CDX2 and COX2 can repress the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| PPA receptor alpha (PPARA) | Colorectal cancer | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | PPARA-PTGS2 interaction | [23] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | HT-29 cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | PPA receptor alpha (PPARA) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between PPARA and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| PPA receptor gamma (PPARG) | Colorectal cancer | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | PPARG-PTGS2 interaction | [23] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | HT-29 cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | PPA receptor gamma (PPARG) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between PPARG and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Transcription factor Sp1 (SP1) | Colorectal cancer | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | SP1-PTGS2 interaction | [24] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Colon cancer cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Transcription factor Sp1 (SP1) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between SP1 and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ICD-11: 2C10 Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 2 HOSPPI | ||||
| Transcription-factor regulation | |||||
| High mobility group A1 (HMGA1) | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | HMGA1-PTGS2 interaction | [25] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | BxPC-3, HPAF-II, MiaPaCa Panc1, PL45 and XPA-3 cell lines | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | High mobility group A1 (HMGA1) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between HMGA1 and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Non-coding RNA regulation | |||||
| hsa-miR-143-3p | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-143-3p--PTGS2 regulation | [26] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | BxPC-3 cell line | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-143-3p is reported to suppress PTGS2 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of PTGS2 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ICD-11: 2C12 Liver cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| Non-coding RNA regulation | |||||
| hsa-miR-16-5p | Liver cancer | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-16-5p--PTGS2 regulation | [27] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | WRL68, HepG2 and Hep3B cell lines | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-16-5p is reported to suppress PTGS2 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of PTGS2 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ICD-11: 2C25 Lung cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 4 HOSPPI | ||||
| Transcription-factor regulation | |||||
| Inhibitor of growth 4 (ING4) | Lung cancer | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | ING4-PTGS2 interaction | [29] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | A549 cell line | ||||
| Description | Inhibitor of growth 4 (ING4) is reported to repress the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between ING4 and COX2 can repress the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Liver activator protein (LAP) | Lung cancer | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | LAP-PTGS2 interaction | [11], [30] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | NCI-H520, NCI-H460, and NCI-H1299 cell lines | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Liver activator protein (LAP) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between LAP and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| STAT 6 (STAT6) | Lung cancer | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | STAT6-PTGS2 interaction | [31] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | A427 and H2122 cell lines | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | STAT 6 (STAT6) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between STAT6 and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Non-coding RNA regulation | |||||
| hsa-miR-589-5p | Lung cancer | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-589-5p--PTGS2 regulation | [28] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | A549 cell line | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-589-5p is reported to suppress PTGS2 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of PTGS2 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ICD-11: 2C60 Breast cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| Transcription-factor regulation | |||||
| Progesterone receptor (PGR) | Breast cancer | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | PGR-PTGS2 interaction | [32] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | T47D and MCF-7 cell lines | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Progesterone receptor (PGR) is reported to repress the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between PGR and COX2 can repress the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ICD-11: 2C73 Ovarian cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 2 HOSPPI | ||||
| Transcription-factor regulation | |||||
| Homeobox protein CDX-1 (CDX1) | Ovarian cancer | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | CDX1-PTGS2 interaction | [33] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | SKOV3 and A2780 cell lines | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Homeobox protein CDX-1 (CDX1) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between CDX1 and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Nuclear receptor family 0 B2 (NR0B2) | Ovarian cancer | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | NR0B2-PTGS2 interaction | [33] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | SKOV3 and A2780 cell lines | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Nuclear receptor family 0 B2 (NR0B2) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between NR0B2 and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ICD-11: 2C77 Cervical cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| Transcription-factor regulation | |||||
| PPA receptor gamma (PPARG) | Cervical cancer | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | PPARG-PTGS2 interaction | [34], [35] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | CaSki cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | PPA receptor gamma (PPARG) is reported to repress the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between PPARG and COX2 can repress the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ICD-11: 2C82 Prostate cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 2 HOSPPI | ||||
| Transcription-factor regulation | |||||
| Androgen receptor (AR) | Prostate cancer | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | AR-PTGS2 interaction | [36] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | LNCaP and PC-3 cell lines | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Androgen receptor (AR) is reported to repress the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between AR and COX2 can repress the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Non-coding RNA regulation | |||||
| hsa-miR-26a-5p | Prostate cancer | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-26a-5p--PTGS2 regulation | [37] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | LNCaP cell line | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-26a-5p is reported to suppress PTGS2 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of PTGS2 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ICD-11: 2E60 Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 2 HOSPPI | ||||
| Non-coding RNA regulation | |||||
| hsa-miR-101-3p | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-101-3p--PTGS2 regulation | [38] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | EC9706 cell line | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-101-3p is reported to suppress PTGS2 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of PTGS2 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| hsa-miR-144-3p | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-144-3p--PTGS2 regulation | [39] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | EC9706 cell line | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-144-3p is reported to suppress PTGS2 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of PTGS2 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ICD-11: 2E64 Skin cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 3 HOSPPI | ||||
| Transcription-factor regulation | |||||
| Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) | Epidermoid carcinoma | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | HDAC4-PTGS2 interaction | [40] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | A431 cell line | ||||
| Description | Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) is reported to deacetylate the COX2 gene and thereby represses the transcriptional activity of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between HDAC4 and COX2 can inhibit the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Liver activator protein (LAP) | Epidermoid carcinoma | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | LAP-PTGS2 interaction | [40] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | A431 cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Liver activator protein (LAP) is reported to repress the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between LAP and COX2 can repress the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Transcription factor AP-1 (JUN) | Epidermoid carcinoma | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | JUN-PTGS2 interaction | [11], [14], [41] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | A431 cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Transcription factor AP-1 (JUN) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between JUN and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ICD Disease Classification 11 Circulatory system diseases | |||||
| ICD-11: BA6Z Myocardial ischemia | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 2 HOSPPI | ||||
| Transcription-factor regulation | |||||
| STAT 1-alpha/beta (STAT1) | Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | STAT1-PTGS2 interaction | [42] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | STAT 1-alpha/beta (STAT1) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between STAT1 and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| STAT 2 (STAT2) | Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | STAT2-PTGS2 interaction | [42] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury cell line | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | STAT 2 (STAT2) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between STAT2 and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ICD Disease Classification 12 Respiratory system diseases | |||||
| ICD-11: CA23 Asthma | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 2 HOSPPI | ||||
| Transcription-factor regulation | |||||
| Nuclear factor kappa-B p105 (NFKB1) | Asthma | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | NFKB1-PTGS2 interaction | [43], [3] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Nasal polyps from aspirin-intolerant asthma/rhinitis patients | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Nuclear factor kappa-B p105 (NFKB1) is reported to repress the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between NFKB1 and COX2 can repress the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Transcription factor p65 (RELA) | Asthma | Repression | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | RELA-PTGS2 interaction | [43], [3] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Nasal polyps from aspirin-intolerant asthma/rhinitis patients | ||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Description | Transcription factor p65 (RELA) is reported to repress the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between RELA and COX2 can repress the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| ICD Disease Classification 15 Musculoskeletal system diseases | |||||
| ICD-11: FA00 Osteoarthritis | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 2 HOSPPI | ||||
| Transcription-factor regulation | |||||
| Protein Dr1 (DR1) | Osteoarthritis | Activation | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | DR1-PTGS2 interaction | [45] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Synovial lining cell linr | ||||
| Description | Protein Dr1 (DR1) is reported to activate the transcription of COX2 gene, which leads to an increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. As a result, the interaction between DR1 and COX2 can activate the drug-metabolizing process of Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
| Non-coding RNA regulation | |||||
| hsa-miR-199a-3p | Osteoarthritis | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-199a-3p--PTGS2 regulation | [44] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Osteoarthritis chondrocytes | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-199a-3p is reported to suppress PTGS2 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of PTGS2 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. | ||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.

