1. Search for Drug Metabolizing Enzyme Entries
In the field of "Search for Drug Metabolizing Enzyme Entries", users can find drug metabolizing enzymes (DME) by searching DME name, drug name, species name, disease name and so on among the entire textual component of INTEDE. Query can be submitted by entering keywords into the main searching frame. The resulting webpage displays profiles of all the DMEs directly related to the search term, including DME ID, DME name, species name, interactome and representative drug.
By clicking the three hyperlinks (MICBIO, XEOTIC and HOSPPI) in "Interactome" column, the interactome diagram for the DME will be displayed. The detailed DME information and drug information can be recursively searched by clicking "DME Info" and "Drug Info", respectively.
DME information can be further accessed via crosslink to UniProtKB, KEGG, Brenda and Gene Database from the following search field. Moreover, users can search by putting DME, drug or other information together into the text field (separated by space or tab) for narrowing the search results.
To facilitate a more customized input query, the wild characters of "*" and "?" are also supported in INTEDE.
(1). If search: "CYP3A", finds 4 entries with gene names including "CYP3A4", "CYP3A5", "CYP3A7" and "CYP3A43";
(2). If search: "UGT1A1", finds single entry with DME named as " UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 (UGT1A1)";
(3). If search: "Apixaban", finds 6 entries of DME metabolizing the drug "Apixaban";
(4). If search: "Shigella flexneri", finds 2 entries of DME encoded by Shigella flexneri species;
(5). If search: "Uterine cancer", finds 6 entries of DME metabolizing anti-uterine cancer drugs;
(6). If search: "Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase ?", finds DME entries named as "Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 1" and "Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 2". Also, these entries whose synonyms include "Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase" will also be shown. Here "?" represents any single character;
(7). If search: "Cytochrome P450 *", finds all CYP450 entries. Here "*" represents an arbitrary string.
For example: if you want to know the detail information of cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2), you can search it by typing “Cytochrome P450 1A2” in the “Search for Drug Metabolizing Enzyme Entries” field. The brief information of human cytochrome P450 1A2 will be provided.
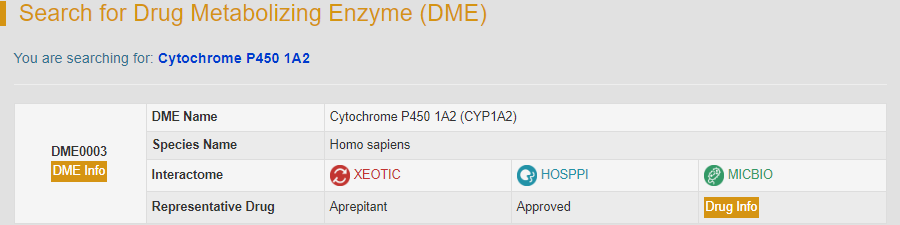
By clicking the “DME Info” button, the detailed information page of CYP1A2 will be displayed. “General Information of DME” section displays the general information of CYP1A2 including its name, synonyms, gene name, uniport ID, lineage, interactome and so on.
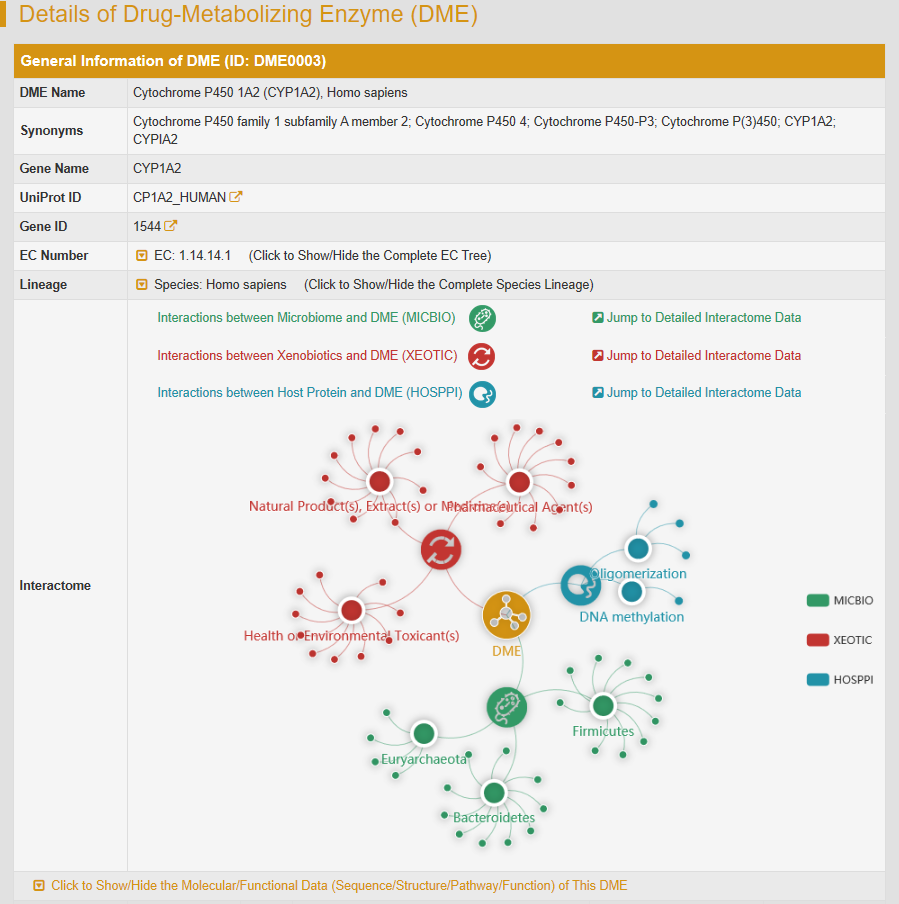
There are three types of interaction in interactome diagram, namely interactions between microbiome and DME (MICBIO), interactions between xenobiotics and DME (XEOTIC) and interactions between host protein and DME (HOSPPI). The yellow icon in the center represents the DME, the green icon with a bacterial outline inside it representes microbiome, the red icon refers to xenobiotics and the dark blue icon refers to host interacting proteins. As the mouse moves over the circles, brief descriptions of what the circles represent are displayed. The hyperlinks in these brief descriptions link to specific information pages. The molecular/functional data of CYP1A2 are also provided in the drop-down list below the interactome diagram.
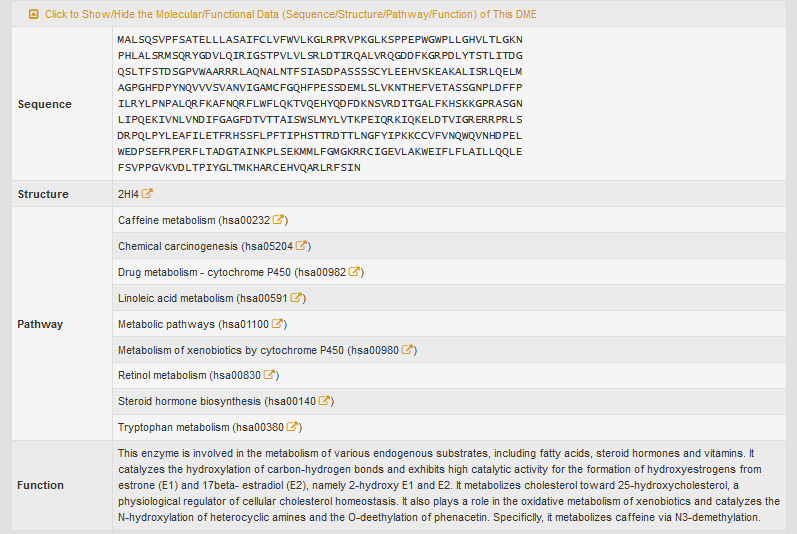
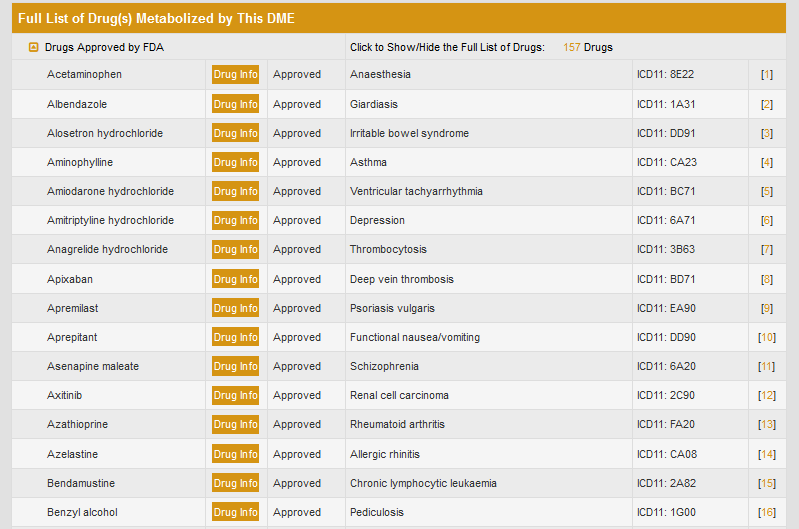
“Full List of Drug(s) Metabolized by This DME” section classifies all the drugs that are metabolized by CYP1A2 into seven classes.
If a class of drugs is selected, the entire list of drugs will be displayed.
“Tissue/Disease-Specific Protein Abundances of This DME” section includes histograms of tissue specific CYP1A2 protein expression in healthy individuals and violin diagrams of CYP1A2 protein abundance in diseased tissues in various disease states. All the expression profiles are downloadable in INTEDE.

Three indexes are used to quantitatively compare the differences in DME expression level between patients and healthy individuals, namely p-value, Fold change and Z-score.

2. Search Drug Metabolizing Enzyme by DME Species-Name Pair
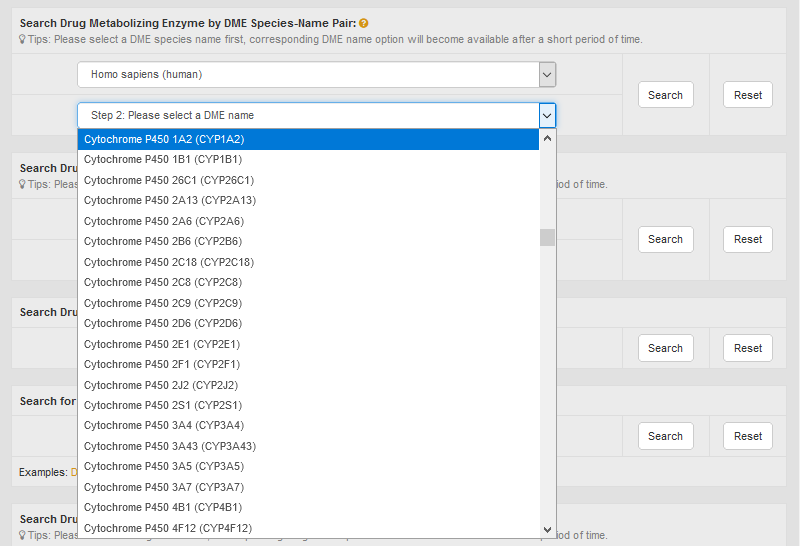
Alternatively, in the field of “Search Drug Metabolizing Enzyme by DME Species-Name Pair”, users can find DME entries by searching species-DME name pair among the entire textual component of INTEDE. First, users should select a specific species from the drop-down list in the first column. Then corresponding DME name option will become available after a short period of time. By clicking “Search” button, the brief information of the selected DME from specific species will be shown.
For example, if you want to know the detail information of human cytochrome P450 1A2, you can select “Homo sapiens (human)” in the “Step 1: Please select a species name” column and then select “Cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2)” in the “Step 2: Please select a DME name” drop-down list.
After clicking the “Search” button, the brief information of human cytochrome P450 1A2 will be provided.
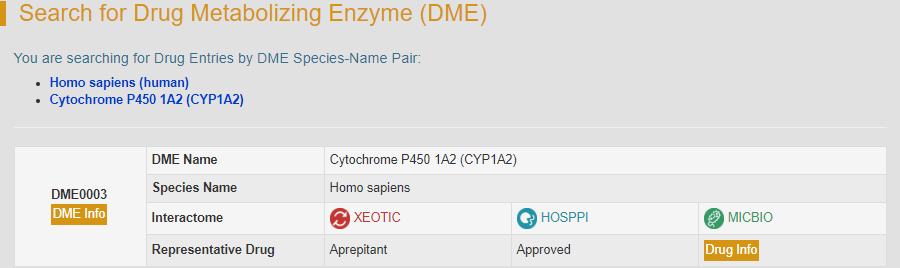
By clicking the “DME Info” button, the detailed information page of CYP1A2 will be displayed.
3. Search Drug Metabolizing Enzyme by Drug Status-Name Pair
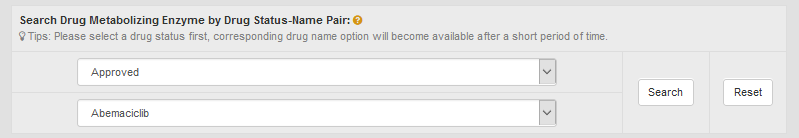
In the field of “Search Drug Metabolizing Enzyme by Drug Status-Name Pair”, users can find DME entries by searching drug status-name pair among the entire textual component of INTEDE. This field divides all drugs into 10 classes (Approved, Phase 4, Phase 3, Phase 2/3, Phase 2, Phase 1/2, Phase 1, Preclinical, Investigative and Discontinued). First, users should select a particular drug status from the drop-down list in the first column. Then corresponding drug name option will become available. By clicking “Search” button, all DME entries metabolizing the selected drug will be displayed.
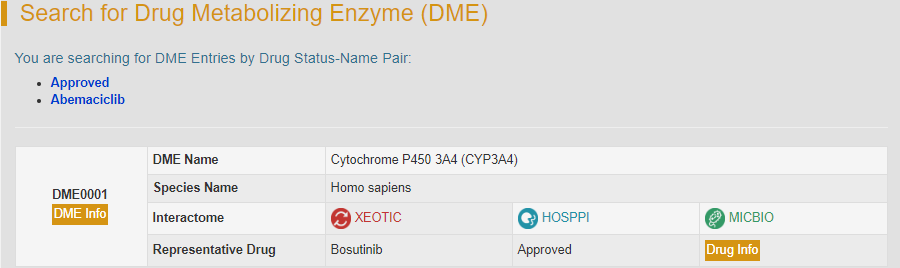
For example, if you want to know the metabolic information of abemaciclib, you can select the second drug “Abemaciclib” under the “Approved” option.
Search result shows abemaciclib is metabolized by Cytochrome P450 3A4 (DME0001), and the representative drug metabolized by this enzyme is Bosutinib. “DME Info” button links to the detailed information page of CYP3A4.
4. Search Drug Metabolizing Enzyme by ICD-11 Defined Disease Class
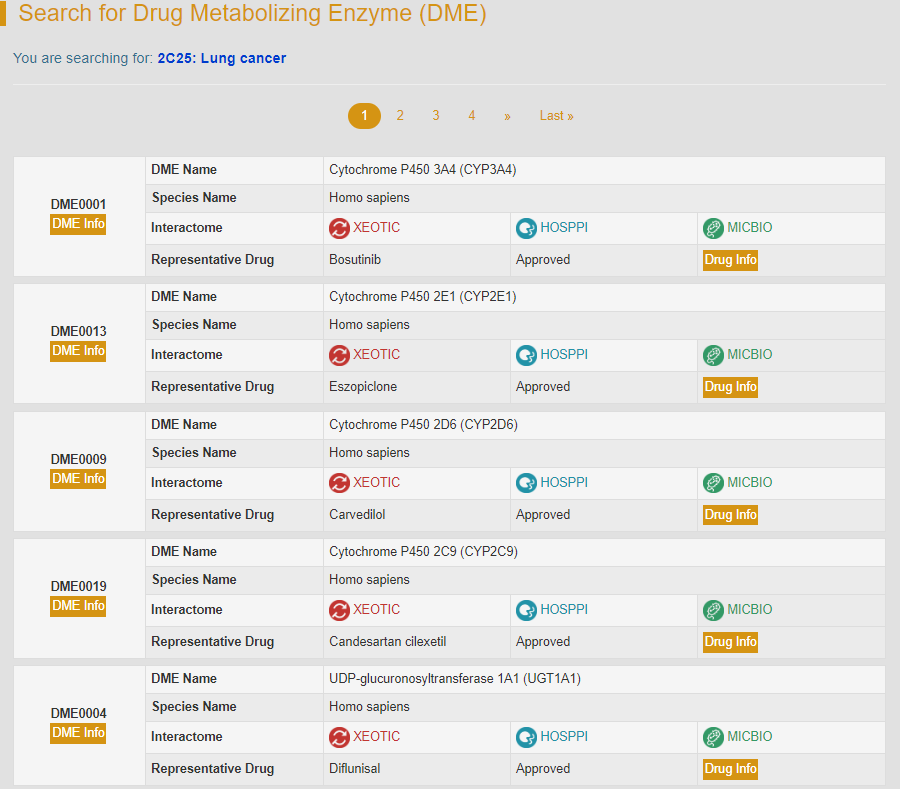
In this field, users can search INTEDE enzyme entries related to a specific disease or an ICD-11-CM code. There is an urgent need to enable data retrieval by using the widely used International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes for facilitating broader, more convenient and automatic data access, processing and exchange by the bench-to-clinic communities, particularly non-domain experts. ICD has been developed by the World Health Organization (WHO), sponsored by the United Nations, adopted by >110 countries and used by physicians, researchers, nurses, health workers, health information managers, policy makers, insurers and health program managers for defining and studying diseases, monitoring and managing health care and allocating resources. In INTEDE, users can search INTEDE enzyme entries by selecting a certain ICD code from the drop-down list.
For example: if search “2C25: Lung cancer”, users can access to various entries of DME metabolizing anti-lung cancer drugs.
5. Search for Drug Entries
Users can identify the metabolized drug entry by searching drug name, DME name, DME gene name, disease name of the metabolized drug and so on among the entire textual component of VARIDT. Query can be submitted by entering keywords into the main searching frame. Users can specify part/full drug name, DME name or any other related information in the text field. The resulting webpage displays profiles of all drugs directly related to the search keywords, including drug structure, drug name, drug status, disease and drug ID. Moreover, user can search by putting drug, DME or other information together into the text field (separated by space or tab) for narrowing the output results. To facilitate a more customized input query, the wild characters of “*” and “?” are supported in INTEDE.
(1). If search: “Amoxicillin”, finds single entry of drug amoxicillin;
(2). If search: “Cytochrome P450 2C9”, finds various entries of drug metabolized by the human DME “Cytochrome P450 2C9”;
(3). If search: “Essential hypertension”, finds various entries of drug for treating the disease “Essential hypertension”;
(4). If search: “Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase ?”, finds a variety of drug entries metabolized by the DMEs named as “Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 1” and “Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 2”. Here “?” represents any single character;
(5). If search: “Cytochrome P450 *”, finds all the drugs metabolized by CYP450. Here “*” represents an arbitrary string.
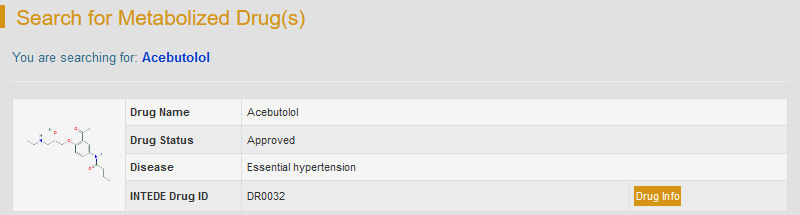
For example: if you want to know the information of drug acebutolol, you can type “Acebutolol” in the “Search for Drug Entries” field. The brief information of acebutolol will be displayed.
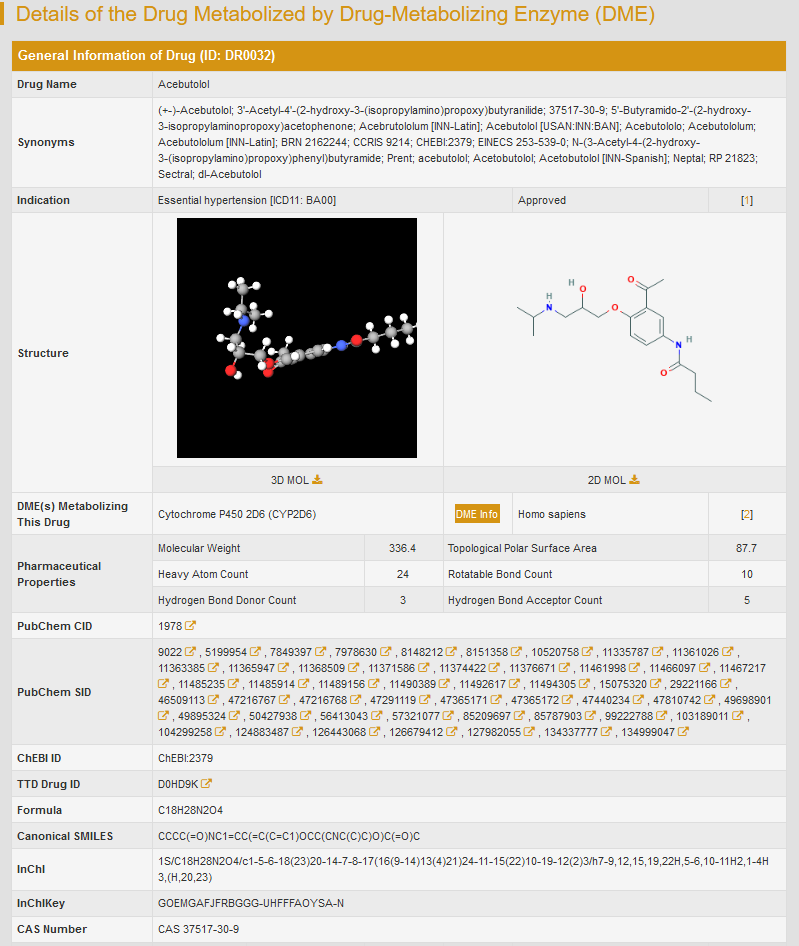
By clicking “Drug Info”, the detailed drug information will be displayed, including basic chemical information and the list of DMEs metabolizing this drug. The information of drug can be further accessed via crosslink to PubChem, ChEBI and TTD from the resulting webpage. If you want the information about the DMEs that metabolize this drug, just click the “DME Info” button.
6. Search Drug Entries by DME Species-Name Pair
Alternatively, in the field of “Search for Drug Entries by DME Name”, users can find drug entries by searching species-DME name pair among the entire textual component of INTEDE. First, users should select a specific species from the drop-down list in the first column. Then corresponding DME name option will become available after a short period of time. By clicking “Search”, the brief information of drugs metabolized by the selected DME from specific species will be shown.
7. Search Drug by Drug Type and Drug Name
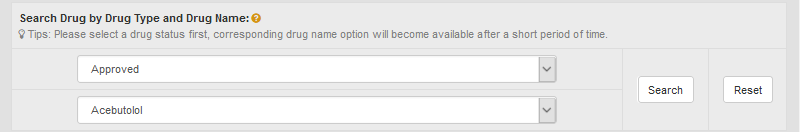
In the field of “Search Drug by Drug Type and Drug Name”, users can find drug entries by searching drug status and drug name among the entire textual component of INTEDE. This field divides all drugs into 10 classes (Approved, Phase 4, Phase 3, Phase 2/3, Phase 2, Phase 1/2, Phase 1, Preclinical, Investigative and Discontinued). First, users should select a particular drug status from the drop-down list in the first column. Then corresponding drug name option will become available. By clicking “Search” button, the selected drug entry will be displayed.
For example, select “Approved” in the “Step 1: Please select a drug type” drop-down list, and chose the fifth drug “Acebutolol”.
Search result will provide brief drug information and a thumbnail image of drug structure. “Drug Info” button links to the detailed drug information page.
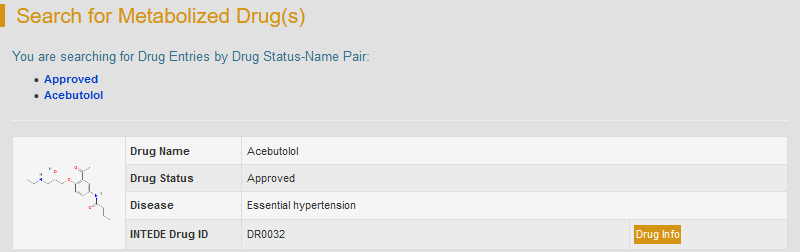
By clicking “Drug Info”, the detailed drug information will be displayed.
8. Search Drug by ICD-11 Defined Disease Class
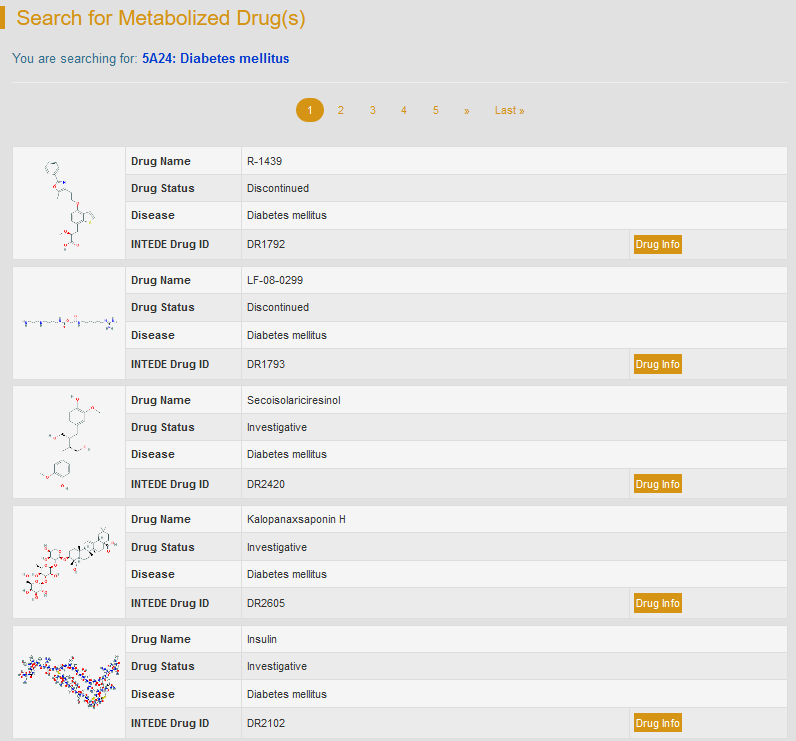
In this field, users can search INTEDE drug entries related to a specific disease or an ICD-11 code. Users can search INTEDE drug entries by selecting a certain ICD code from the drop-down list. The resulting webpage will display a list of drugs used to treat the selected disease and their brief information. By clicking “Drug Info”, the detailed drug information will be displayed.
For example: if search “5A24: Diabetes mellitus”, users can access to various entries of drug for the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
9. Search for Interactions between Microbiome and Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (MICBIO)
In this field, users can find interactions between microbiome and drug-metabolizing enzyme by searching DME name, drug name, species name, disease name and so on among the entire textual component of INTEDE. Query can be submitted by entering keywords into the main searching frame. The resulting webpage displays profiles of all the DMEs directly related to the search term, including DME ID, DME name, species name, interactome and representative co-metabolized drug. Moreover, to facilitate a more customized input query, the wild characters of “*” and “?” are supported in INTEDE.
For example, if you search “Bacteroides finegoldii”, various DMEs which interplay with Bacteroides finegoldii will be displayed.

By clicking the hyperlink “MICBIO” of DME0001, general information of the selected DME and the interactome diagram for the DME will be displayed. “DME Info” links to the detailed DME information page.

The detailed interactions between CYP3A4 and microbiome are classified according to the phylum of species.
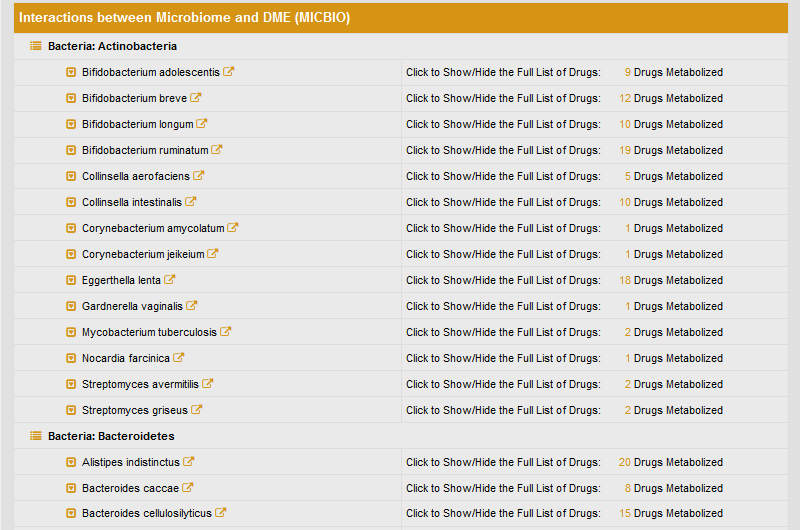
If click a specific species name, such as Bifidobacterium adolescentis, the list of drugs co-metabolized by this species and CYP3A4 will be displayed. The description of this interactome is given by clicking the drug name.

10. Search for MICBIO by Microbiome Species Name
In this field, users can search MICBIO by microbiome species name from the drop-down list. For example, if you select the third species “Acidaminococcus intestini”, the unique DME0021 interplaying with Acidaminococcus intestine will be displayed. Similarly, by clicking “MICBIO” button, you can get access to the detailed interaction information page.

11. Search for MICBIO by Drug Metabolizing Enzyme Name
In this field, users can search MICBIO by host DME name from the drop-down list. For example, if you select “Cytochrome P450 2A6 (CYP2A6)”, the “MICBIO” of CYP2A6 will be displayed. By clicking “MICBIO” button, you can get access to the detailed interaction information page.
12. Search MICBIO by Co-effect Drug Status-Name Pair
In the field of “Search MICBIO by Co-effect Drug Status-Name Pair”, users can find MICBIO entries by searching drug status-name pair among the entire textual component of INTEDE. This field divides all drugs into 10 classes (Approved, Phase 4, Phase 3, Phase 2/3, Phase 2, Phase 1/2, Phase 1, Preclinical, Investigative and Discontinued). First, users should select a particular drug status from the drop-down list in the first column. Then corresponding drug name option will become available after a short period of time.
For example, if you want to know the MICBIO information of aspirin, you can select “Aspirin” under the “Approved” option. Search result shows six human DMEs which can co-metabolize aspirin with human microbiome, and the “MICBIO” links to detailed interaction information page.
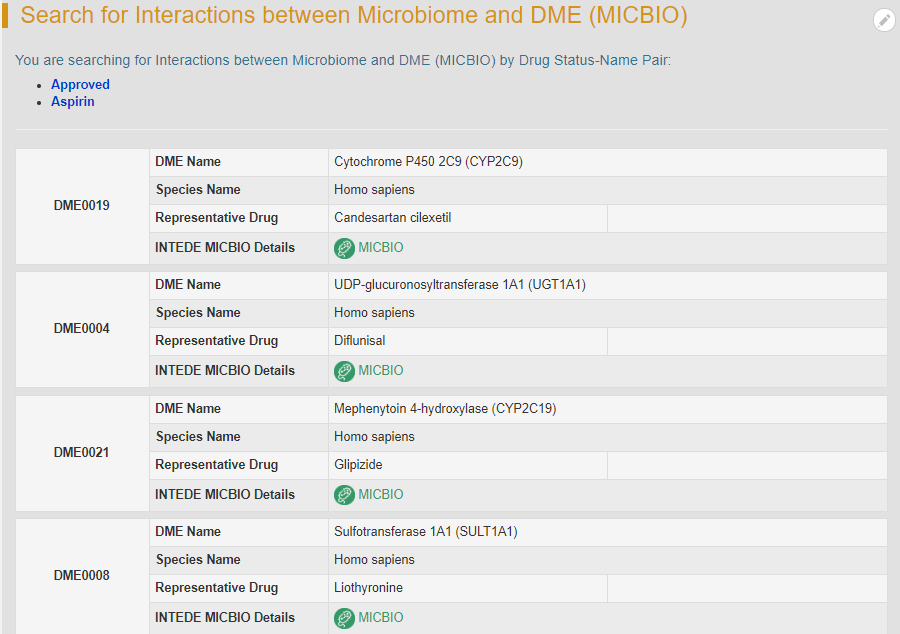
13. Search MICBIO by ICD-11 Defined Disease Class
In this field, users can search MICBIO information by selecting a certain ICD code from the drop-down list. For example: if search “2B90: Colon cancer”, users can access to various entries of DMEs which can co-metabolize anti-colon cancer drugs with human microbiome.
14. Search for Interactions between Xenobiotics and Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (XEOTIC)
In this field, users can find interactions between microbiome and drug-metabolizing enzyme by searching DME name and xenobiotics name among the entire textual component of INTEDE. The resulting webpage displays profiles of all the DMEs directly related to the search term, including DME ID, DME name, species name, interactome and representative drug. Moreover, to facilitate a more customized input query, the wild characters of “*” and “?” are supported in INTEDE.
For example, if you search “Oxyquinoline”, five DMEs which interplay with oxyquinoline will be displayed.
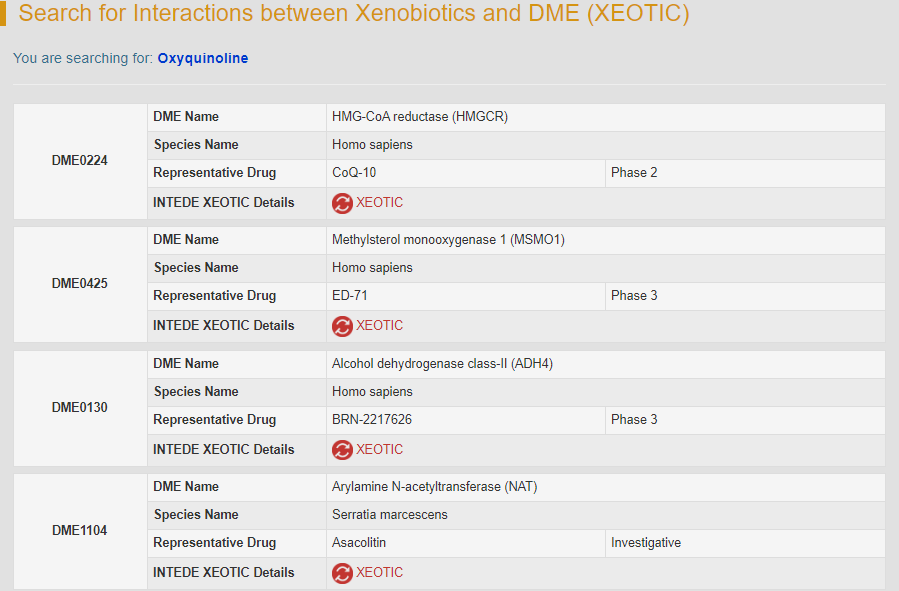
By clicking the hyperlink “XEOTIC” of DME0224, general information of the selected DME and the interactome diagram for the DME will be displayed. “DME Info” links to the detailed DME information page.
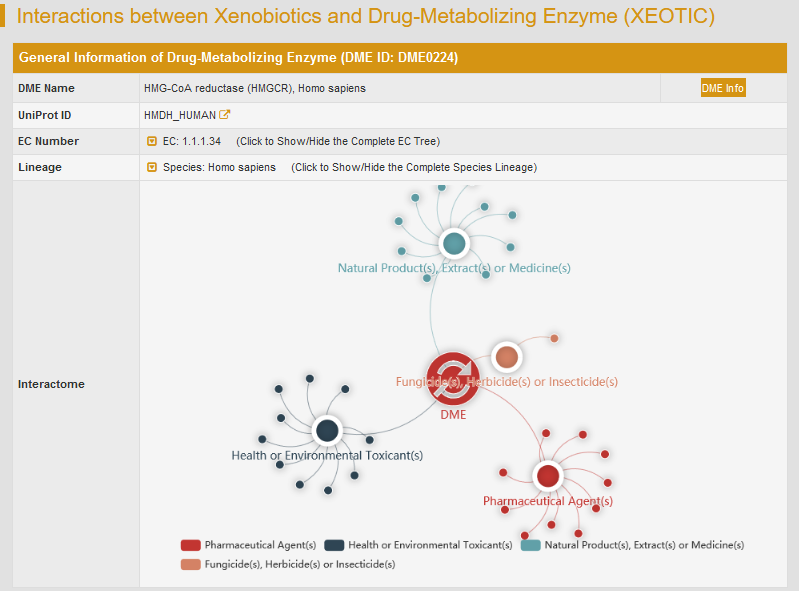
The detailed interactions between human HMG-CoA reductase and xenobiotics are classified according to the type of xenobiotics.

If click a particular xenobiotics class, such as “Acute Toxic Substance”, the list of xenobiotics will be displayed. The effect of oxyquinoline on HMG-CoA reductase is given by clicking the xenobiotics name “Oxyquinoline”.
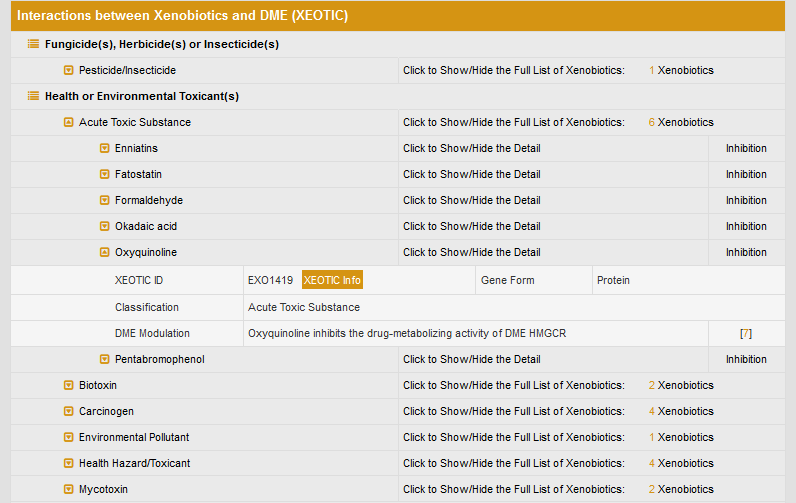
15. Search XEOTIC by Xenobiotics Type-Name Pair
In this field, users can find XEOTIC entries by searching xenobiotics type-name pair among the entire textual component of INTEDE. This field divides all xenobiotics into six classes. The search result displays the DMEs effected by the selected xenobiotics.
16. Search XEOTIC by DME Species-Name Pair
In this field, users can find XEOTIC entries by searching DME species-name pair among the entire textual component of INTEDE. The search result displays the selected DME, and by clicking the hyperlink “XEOTIC”, general information of the selected DME and the interactome diagram for the DME will be displayed.
17. Search XEOTIC by Drug Status-Name Pair
In the field of “Search XEOTIC by Drug Status-Name Pair”, users can find XEOTIC entries by searching drug status-name pair among the entire textual component of INTEDE. This field divides all drugs into 10 classes (Approved, Phase 4, Phase 3, Phase 2/3, Phase 2, Phase 1/2, Phase 1, Preclinical, Investigative and Discontinued). Users should select a particular drug status from the drop-down list in the first column and then choose a drug name.
For example, if you want to know the XEOTIC information of aspirin, you can select “Aspirin” under the “Approved” option. Search result shows the XEOTIC page of human DMEs which can be modulated by xenobiotics. The “XEOTIC” links to detailed interaction information page.
18. Search XEOTIC by ICD-11 Defined Disease Class
In this field, users can search XEOTIC information by selecting a certain ICD code from the drop-down list. For example: if search “2B90: Colon cancer”, users can access to various entries of DMEs which can metabolize anti-colon cancer drugs. The “XEOTIC” button of each DME links to detailed interaction information page.
19. Search for Interactions between Protein and Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (HOSPPI)
In this field, users can find interactions between host protein and DME by searching DME name, drug name, disease name, interacting protein name and so on among the entire textual component of INTEDE. The resulting webpage displays all the DMEs directly related to the search term. Moreover, to facilitate a more customized input query, the wild characters of “*” and “?” are supported in INTEDE.
For example, if you search “Cytochrome b5”, various DMEs whose expression are modulated by Cytochrome b5 will be displayed.
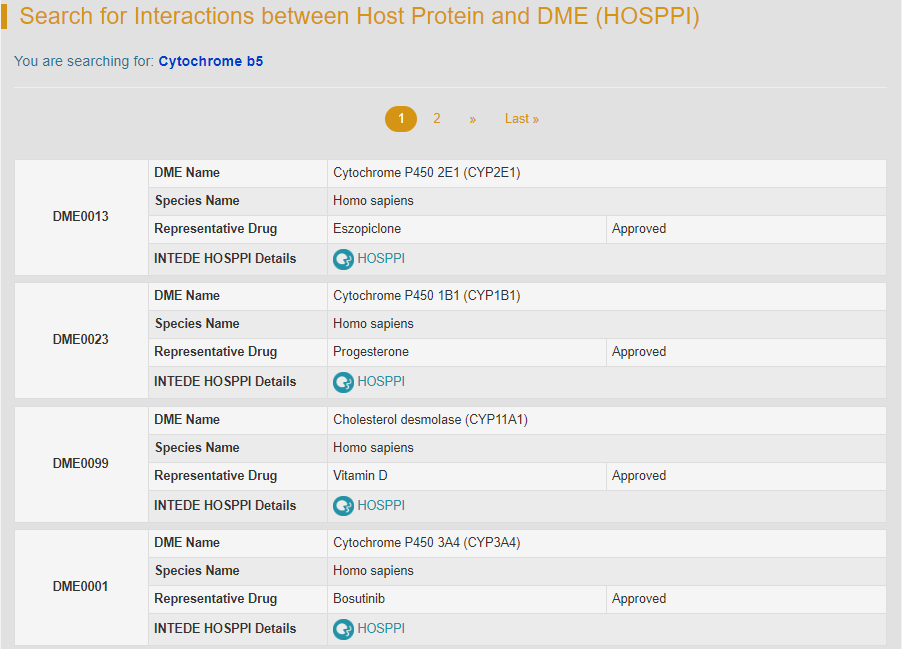
By clicking the hyperlink “HOSPPI” of DME0013, general information of the selected DME and the interactome diagram for this DME will be displayed. “DME Info” links to the detailed DME information page.

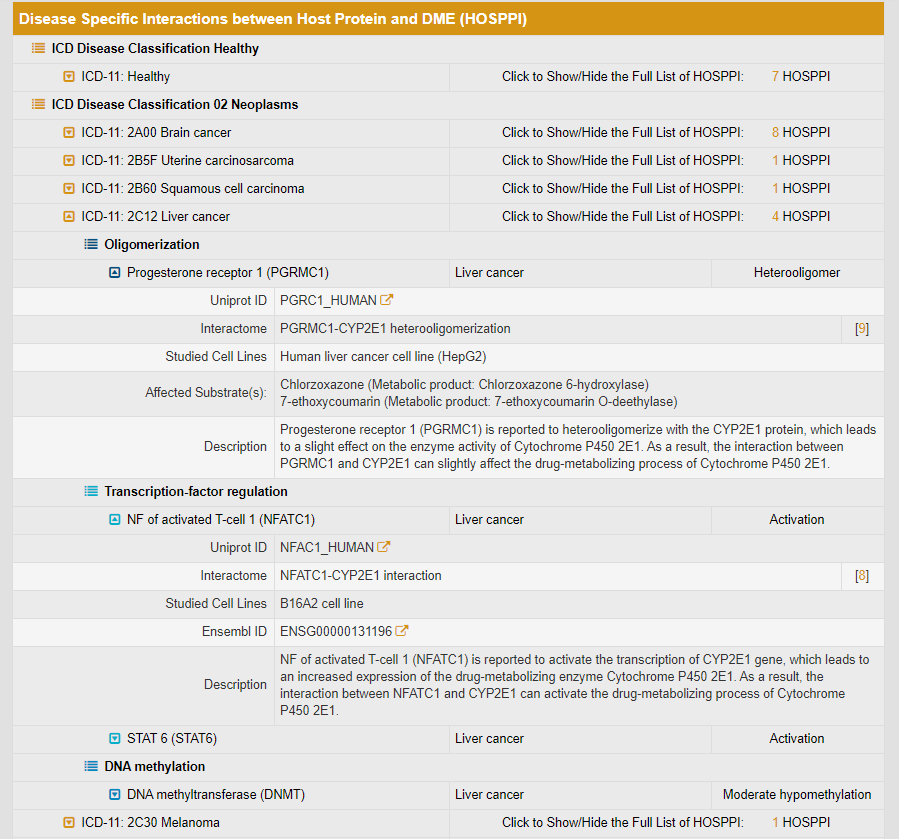
The detailed disease specific interactions between Aromatase (CYP19A1) and host proteins are classified according to ICD disease classification.

If you click on the “ICD-11: 2C60 Breast cancer”, the drop-down list of proteins interacting with CYP19A1 in breast cancer patients will be displayed. “HOSPPI” includes three types: oligomerization, transcription-factor regulation and DNA methylation. Oligomerization module includes proteins which can form oligomers with CYP19A1. This module also displays the affected substrates and the description of oligomerization result. Similarly, transcription factor regulation module includes transcription factors which can regulate the expression of CYP19A1. This module provides more details by linking to UniprotKB and Ensembl database. The result description of transcription-factor regulation is also provided.
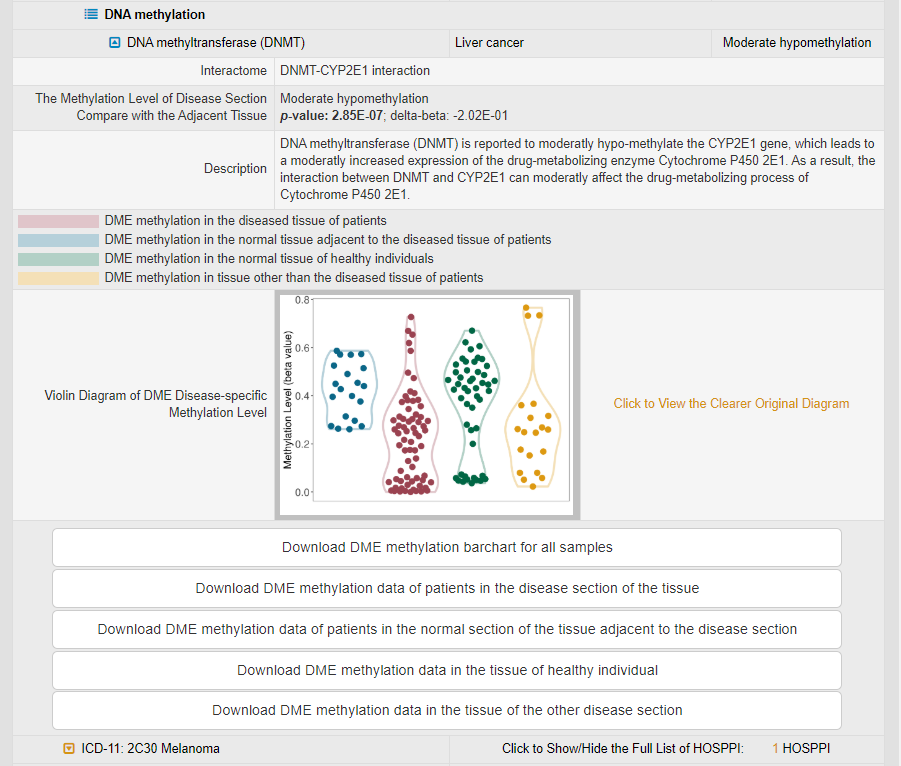
In DNA methylation module, there is only one protein (DNA methyltransferase) interacting with the DME. By calculating p-value and delta-beta, the significance of the difference in methylation level between the disease tissue of patients, the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients, the normal tissue of healthy individuals and the tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients is evaluated (due to the absence of the corresponding sample, only part of them can be calculated under some diseases condition). The result of the effect of DNA methylation on CYP2E1 expression is also described. Moreover, the violin diagram of DME disease-specific methylation level is displayed, which visualizes the difference in gene methylation level between patients and healthy individuals. All DME gene methylation data can be downloaded directly.
20. Search for HOSPPI by Interacting Protein Name
In this field, users can find HOSPPI entries by searching interacting protein name among the entire textual component of INTEDE. The resulting webpage displays the DMEs regulated by the selected interacting protein.
21. Search for HOSPPI DME Species-Name Pair
In this field, users can find HOSPPI entries by searching DME species-name pair among the entire textual component of INTEDE. The search result displays the selected DME, and by clicking the hyperlink “HOSPPI”, general information of the selected DME and the interactome diagram for the DME will be displayed.
22. Search HOSPPI by Drug Status-Name Pair
In the field of “Search HOSPPI by Drug Status-Name Pair”, users can find HOSPPI entries by searching drug status-name pair among the entire textual component of INTEDE. This field also divides all drugs into 10 classes. Users should select a particular drug status from the drop-down list in the first column and then choose a drug name.
For example, if you want to know the HOSPPI information of aspirin, you can select “Aspirin” under the “Approved” option. Search result shows the HOSPPI page of human DMEs which can be modulated by three types of interacting proteins. The “HOSPPI” links to detailed interaction information page.
23. Search HOSPPI by ICD-11 Defined Disease Class
In this field, users can search HOSPPI information by selecting a certain ICD code. For example: if search “1B73: Staphylococcus infection”, users can access to various entries of DMEs which can metabolize anti-Staphylococcus infection drugs and be regulated by interacting proteins. The “HOSPPI” button of each DME links to detailed interaction information page.
23. Download the Full Data of INTEDE from a Variety of Customized Links
INTEDE provides functions for downloading all INTEDE data from various customized links.
(1). The interactome data of DME: (a) microbiome-host DME interaction data (microbiome species name / co-effect drug and result / microbiome family, phylum, etc); (b) xenobiotics factors (health or environmental toxicant / natural product / extract or medicine, etc) altering DME activity data; (c) host protein-DME interaction data (DNA methylation / Transcription-factor regulation / Oligomerization);
(2). Data of sequence, structure, function and cross-matching: (a) data of drug-metabolizing enzyme (sequence (FASTA format) and structure (PDB file) data of DMEs / metabolizing enzyme-drug affinity data / tissue-distribution and function data of DMEs / complete EC Tree of DMEs); (b) data of drugs metabolized by DMEs (2D structure data (SDF format) for the drugs metabolized by DMEs / 3D structure data (SDF format) for the drugs metabolized by DMEs / SMILES and InChI for the drugs metabolized by DMEs / therapeutic classes and physicochemical properties for the drugs); (c) data of xenobiotics that affects DMEs (2D structure data (SDF format) for the xenobiotics that affects DMEs / 3D structure data (SDF format) for the xenobiotics that affects DMEs / sequence for the xenobiotics that affects DMEs); (d) data of synonyms and cross-matching (cross-matching ID between the DMEs and a variety of public databases / synonyms of DMEs and their corresponding drugs / DMEs to disease mapping with International Classification of Diseases (ICD) identifiers / drug to disease mapping with International Classification of Diseases (ICD) identifiers).
All data can be readily downloaded by simply clicking the corresponding “Click to Save” button.

