Details of Host Protein-DME Interaction (HOSPPI)
| General Information of Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME ID: DME0223) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DME Name | Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT1), Homo sapiens | DME Info | |||
| UniProt ID | |||||
| EC Number | EC: 2.4.2.8 (Click to Show/Hide the Complete EC Tree) | ||||
| Lineage | Species: Homo sapiens (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage) | ||||
| Interactome | |||||
| Disease Specific Interactions between Host Protein and DME (HOSPPI) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification 02 Neoplasms | |||||
| ICD-11: 2A00 Brain cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 2 HOSPPI | ||||
| DNA methylation | |||||
| DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) | Brain neuroblastoma | Moderate hypomethylation | |||
| Interaction Name | DNMT-HPRT1 interaction | ||||
| The Methylation Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | Moderate hypomethylation p-value: 9.74E-03; delta-beta: -2.58E-01 | ||||
| Description | DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) is reported to moderatly hypo-methylate the HPRT1 gene, which leads to a moderatly increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. As a result, the interaction between DNMT and HPRT1 can moderatly affect the drug-metabolizing process of Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. | ||||
|
DME methylation in the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
|||||
| Violin Diagram of DME Disease-specific Methylation Level |
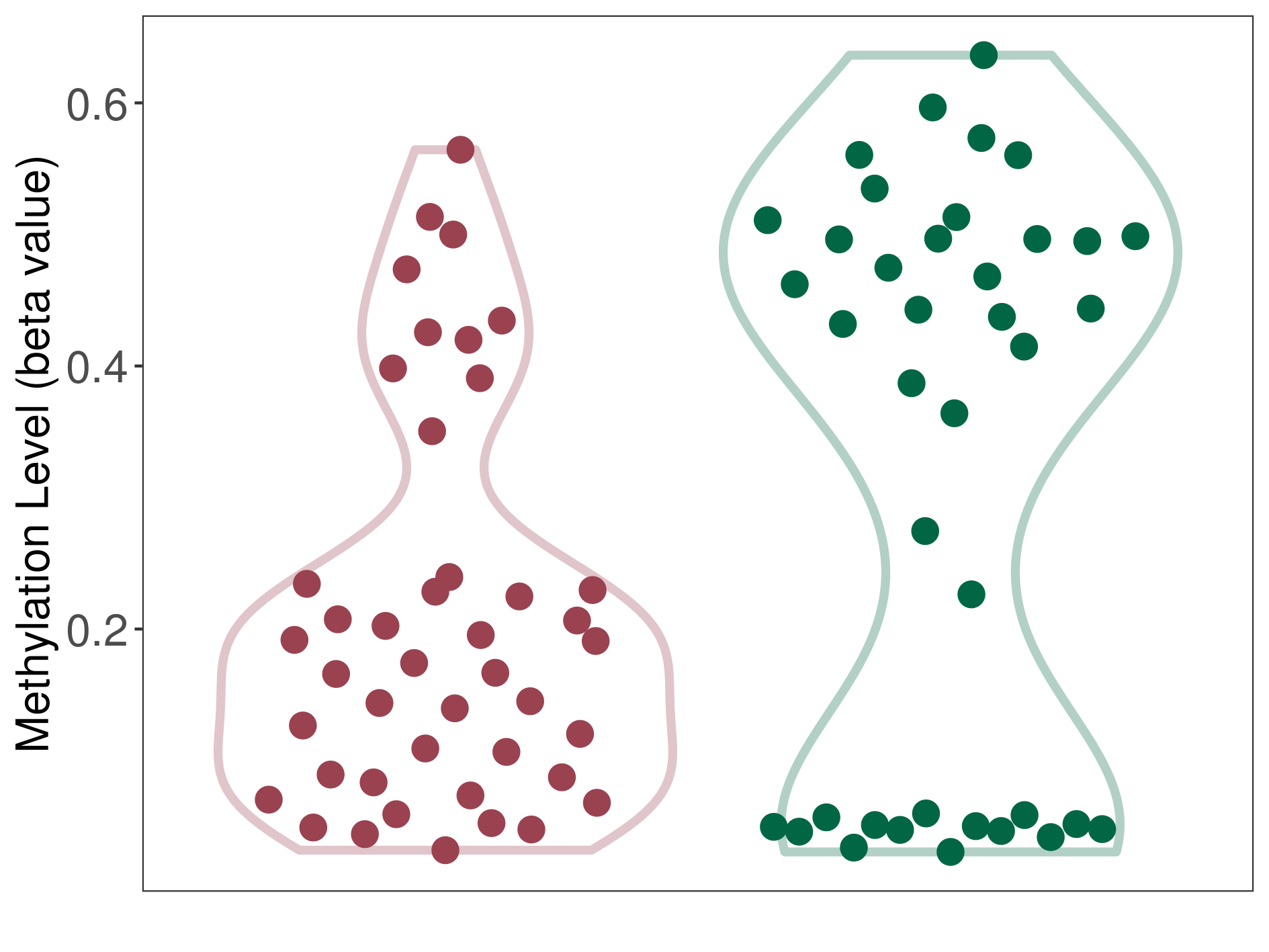
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram | |||
| DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) | Multilayered rosettes embryonal tumour | Significant hypomethylation | |||
| Interaction Name | DNMT-HPRT1 interaction | ||||
| The Methylation Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | Significant hypomethylation p-value: 1.13E-03; delta-beta: -3.03E-01 | ||||
| Description | DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) is reported to significantly hypo-methylate the HPRT1 gene, which leads to a significantly increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. As a result, the interaction between DNMT and HPRT1 can significantly affect the drug-metabolizing process of Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. | ||||
|
DME methylation in the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
|||||
| Violin Diagram of DME Disease-specific Methylation Level |
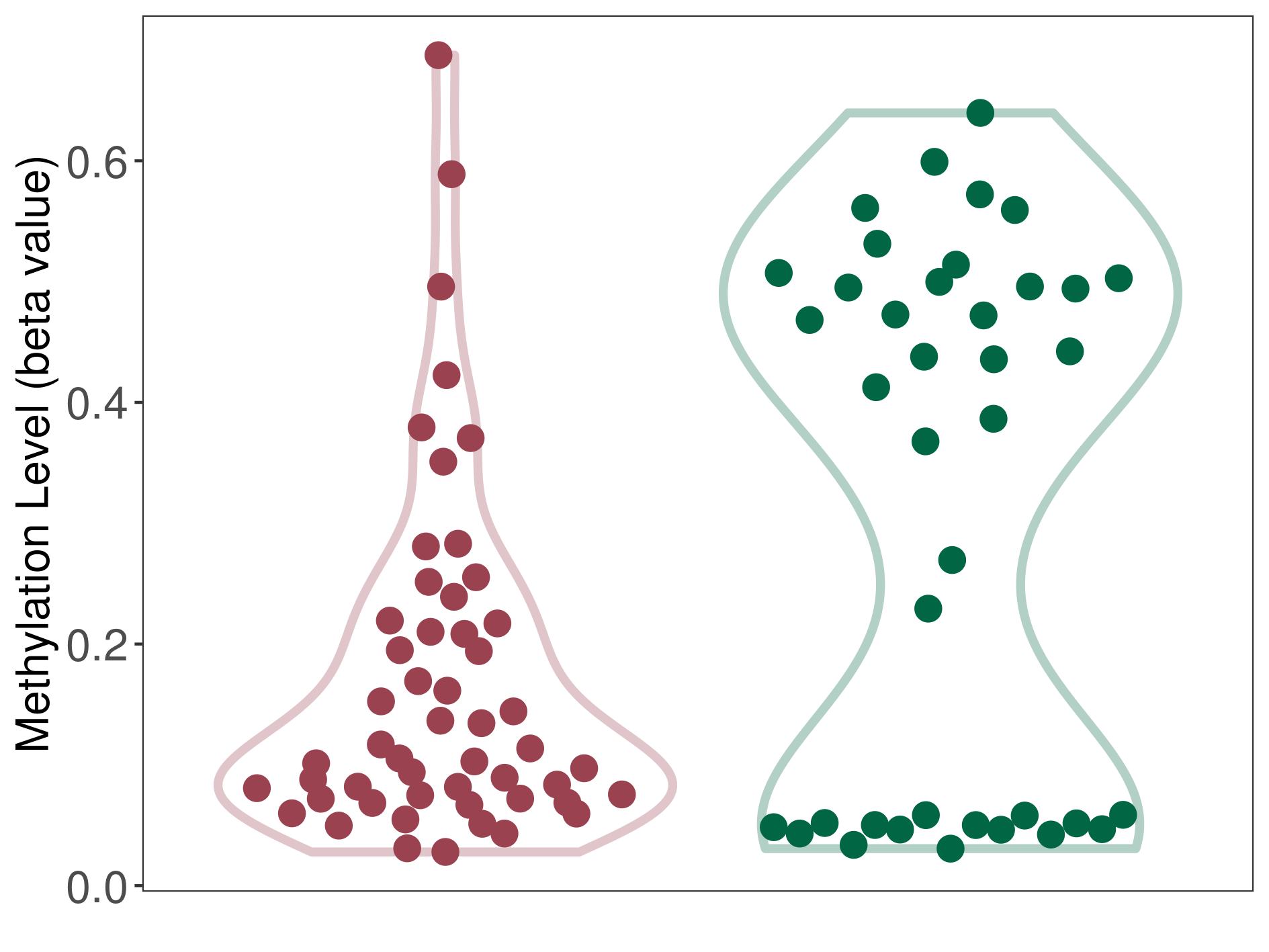
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram | |||
| ICD-11: 2A01 Meningeal tumour | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| DNA methylation | |||||
| DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) | Meningioma | Moderate hypermethylation | |||
| Interaction Name | DNMT-HPRT1 interaction | ||||
| The Methylation Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | Moderate hypermethylation p-value: 1.04E-05; delta-beta: 2.64E-01 | ||||
| Description | DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) is reported to moderatly hyper-methylate the HPRT1 gene, which leads to a moderatly decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. As a result, the interaction between DNMT and HPRT1 can moderatly affect the drug-metabolizing process of Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. | ||||
|
DME methylation in the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
|||||
| Violin Diagram of DME Disease-specific Methylation Level |
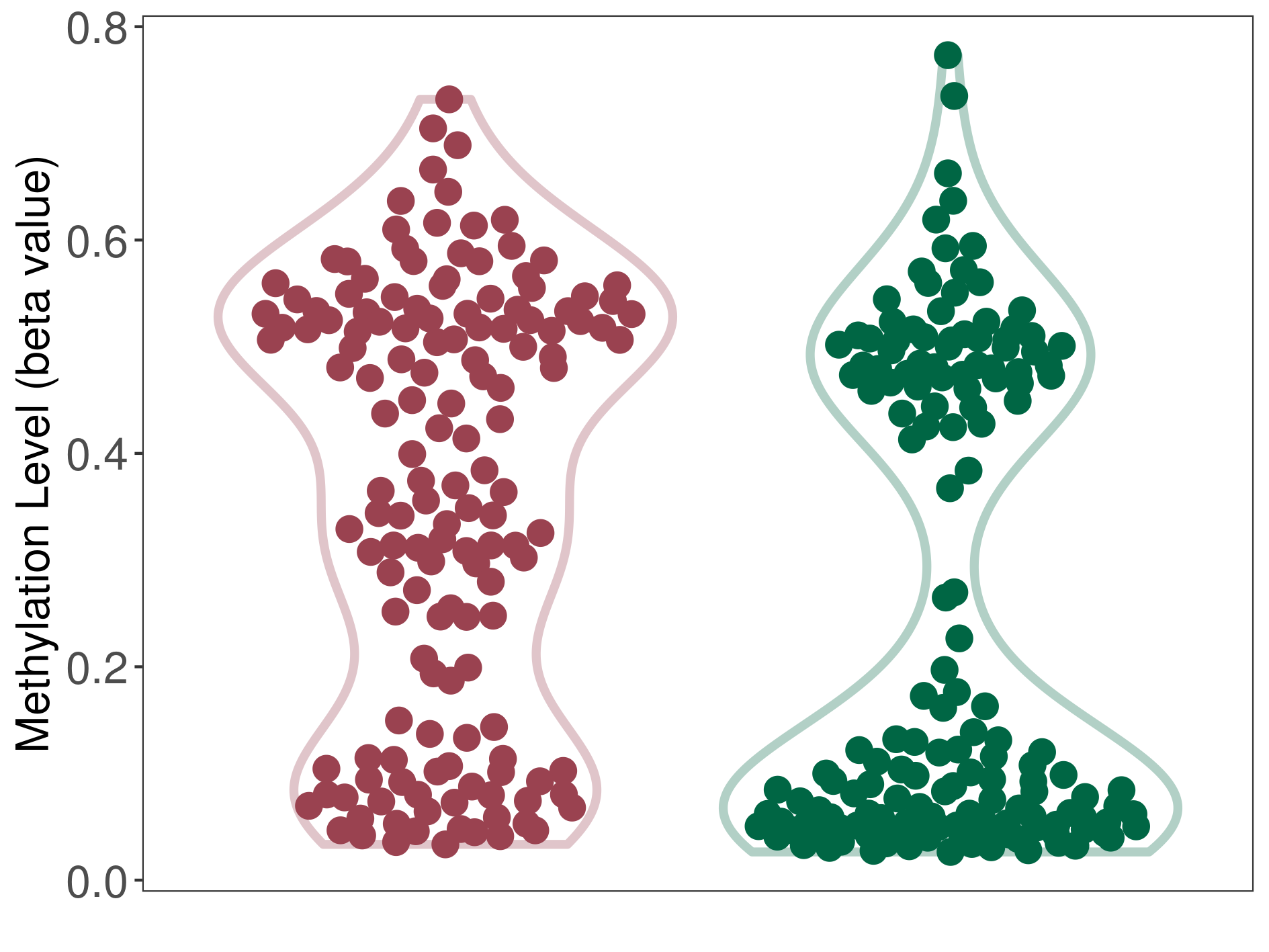
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram | |||
| ICD-11: 2A11 Brain neuroblastoma | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| Oligomerization | |||||
| Aldehyde dehydrogenase 16A1 (ALDH16A1) | Neuroblastoma | Heterooligomer | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | ALDH16A1-HPRT1 heterooligomerization | [1] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | SH-SY5Y cell line | ||||
| Description | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 16A1 (ALDH16A1) is reported to heterooligomerize with the HPRT1 protein, which leads to an increased activity of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. As a result, the interaction between ALDH16A1 and HPRT1 can facilitate the drug-metabolizing process of Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. | ||||
| ICD-11: 2A60 Acute myeloid leukemia | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| DNA methylation | |||||
| DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) | Acute myeloid leukemia | Significant hypermethylation | |||
| Interaction Name | DNMT-HPRT1 interaction | ||||
| The Methylation Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | Significant hypermethylation p-value: 8.70E-05; delta-beta: 3.71E-01 | ||||
| Description | DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) is reported to significantly hyper-methylate the HPRT1 gene, which leads to a significantly decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. As a result, the interaction between DNMT and HPRT1 can significantly affect the drug-metabolizing process of Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. | ||||
|
DME methylation in the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
|||||
| Violin Diagram of DME Disease-specific Methylation Level |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram | |||
| ICD-11: 2B90 Colorectal cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| DNA methylation | |||||
| DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) | Colorectal cancer | Significant hypomethylation | |||
| Interaction Name | DNMT-HPRT1 interaction | ||||
| The Methylation Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | Significant hypomethylation p-value: 9.94E-03; delta-beta: -3.36E-01 | ||||
| Description | DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) is reported to significantly hypo-methylate the HPRT1 gene, which leads to a significantly increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. As a result, the interaction between DNMT and HPRT1 can significantly affect the drug-metabolizing process of Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. | ||||
|
DME methylation in the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
|||||
| Violin Diagram of DME Disease-specific Methylation Level |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram | |||
| ICD-11: 2C12 Liver cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| Oligomerization | |||||
| Aldehyde dehydrogenase 16A1 (ALDH16A1) | Liver cancer | Heterooligomer | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | ALDH16A1-HPRT1 heterooligomerization | [1] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | HepG2 cell line | ||||
| Description | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 16A1 (ALDH16A1) is reported to heterooligomerize with the HPRT1 protein, which leads to an increased activity of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. As a result, the interaction between ALDH16A1 and HPRT1 can facilitate the drug-metabolizing process of Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. | ||||
| ICD-11: 2C25 Lung cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| Oligomerization | |||||
| Aldehyde dehydrogenase 16A1 (ALDH16A1) | Lung cancer | Heterooligomer | |||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | ALDH16A1-HPRT1 heterooligomerization | [1] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | A549 cell line | ||||
| Description | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 16A1 (ALDH16A1) is reported to heterooligomerize with the HPRT1 protein, which leads to an increased activity of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. As a result, the interaction between ALDH16A1 and HPRT1 can facilitate the drug-metabolizing process of Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. | ||||
| ICD-11: 2D50 Brain cancer metastasis | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| DNA methylation | |||||
| DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) | Esthesioneuroblastoma | Moderate hypomethylation | |||
| Interaction Name | DNMT-HPRT1 interaction | ||||
| The Methylation Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | Moderate hypomethylation p-value: 2.79E-02; delta-beta: -2.68E-01 | ||||
| Description | DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) is reported to moderatly hypo-methylate the HPRT1 gene, which leads to a moderatly increased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. As a result, the interaction between DNMT and HPRT1 can moderatly affect the drug-metabolizing process of Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. | ||||
|
DME methylation in the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
|||||
| Violin Diagram of DME Disease-specific Methylation Level |
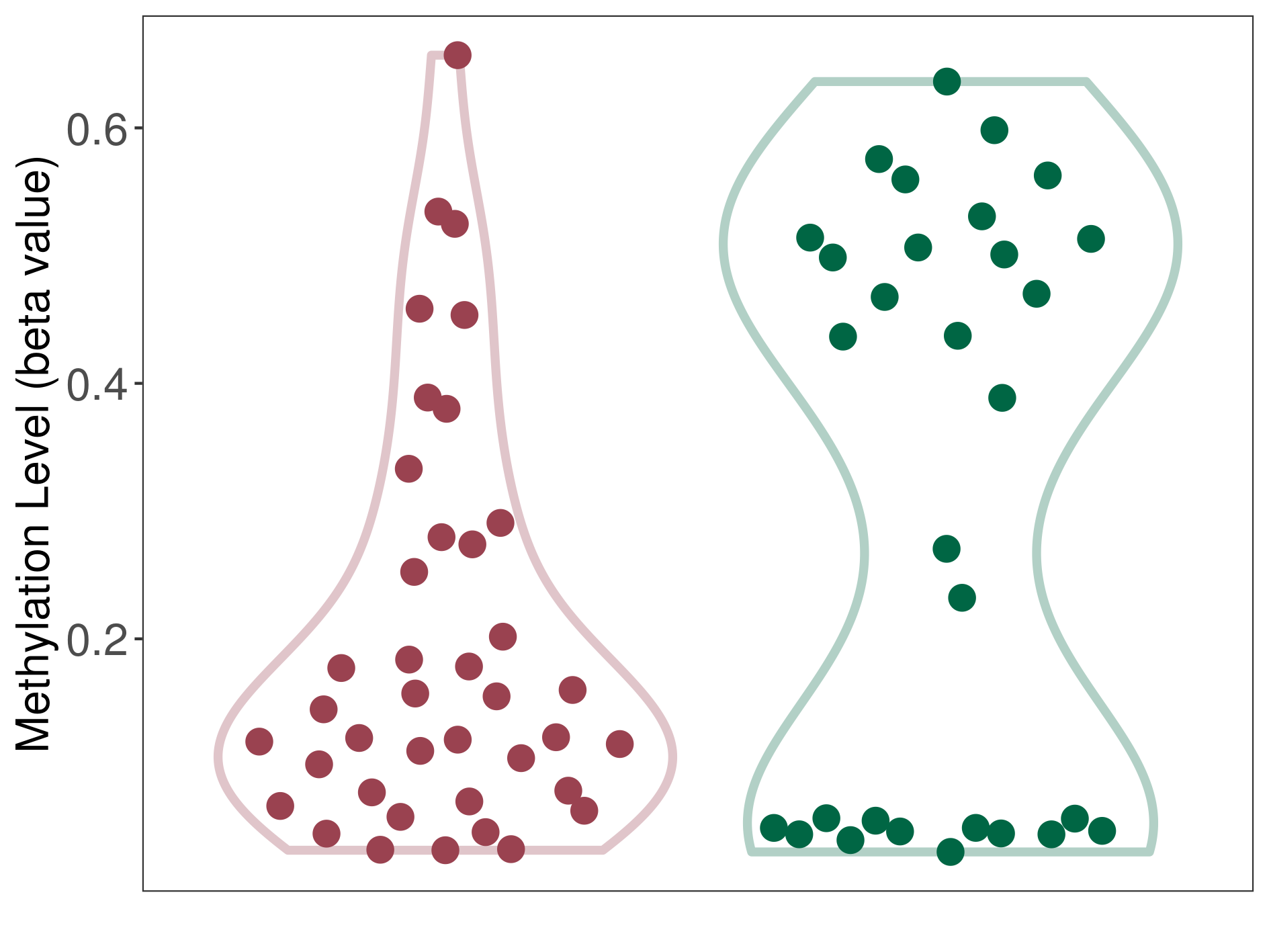
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram | |||
| ICD Disease Classification 05 Endocrine/nutritional/metabolic diseases | |||||
| ICD-11: 5B81 Obesity | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| DNA methylation | |||||
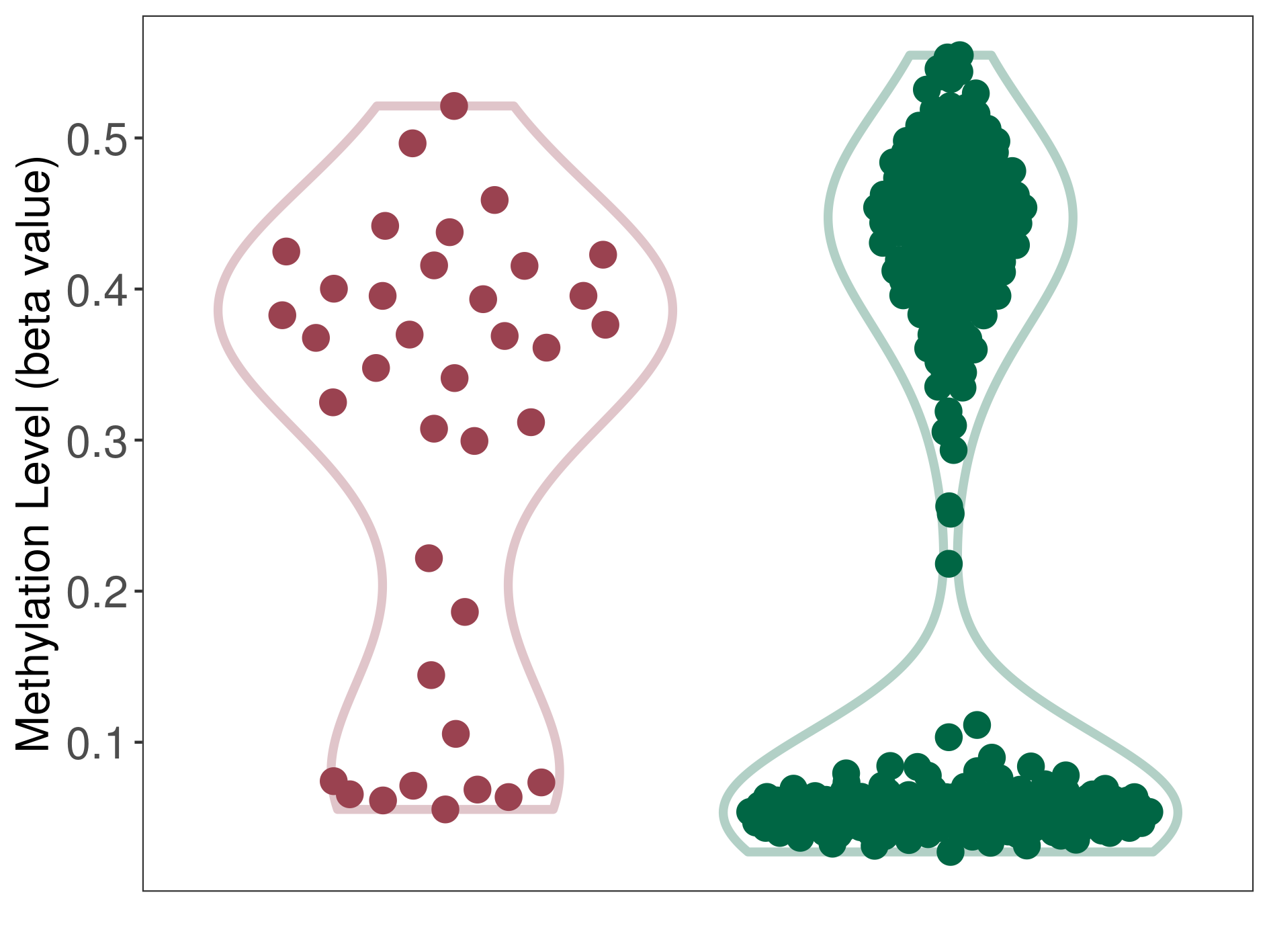
| DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) | Obesity | Moderate hypermethylation | |||
| Interaction Name | DNMT-HPRT1 interaction | ||||
| The Methylation Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | Moderate hypermethylation p-value: 5.22E-03; delta-beta: 2.97E-01 | ||||
| Description | DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) is reported to moderatly hyper-methylate the HPRT1 gene, which leads to a moderatly decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. As a result, the interaction between DNMT and HPRT1 can moderatly affect the drug-metabolizing process of Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. | ||||
|
DME methylation in the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
|||||
| Violin Diagram of DME Disease-specific Methylation Level |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram | |||
| ICD Disease Classification 08 Nervous system diseases | |||||
| ICD-11: 8A20 Alzheimer disease | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| DNA methylation | |||||
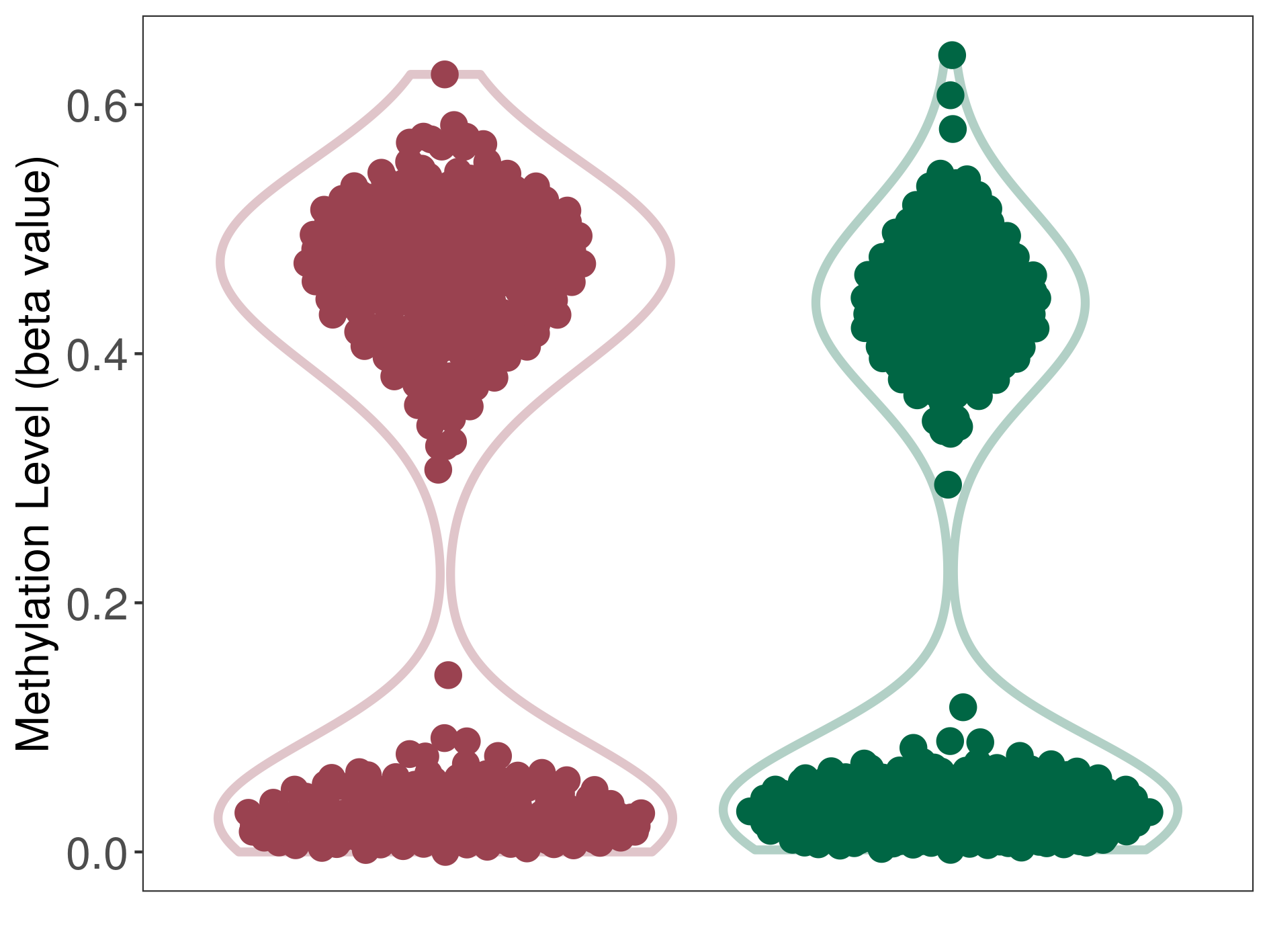
| DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) | Alzheimer disease | Significant hypermethylation | |||
| Interaction Name | DNMT-HPRT1 interaction | ||||
| The Methylation Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | Significant hypermethylation p-value: 5.44E-06; delta-beta: 3.42E-01 | ||||
| Description | DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) is reported to significantly hyper-methylate the HPRT1 gene, which leads to a significantly decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. As a result, the interaction between DNMT and HPRT1 can significantly affect the drug-metabolizing process of Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. | ||||
|
DME methylation in the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
|||||
| Violin Diagram of DME Disease-specific Methylation Level |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram | |||
| ICD-11: 8E49 Postviral fatigue syndrome | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| DNA methylation | |||||
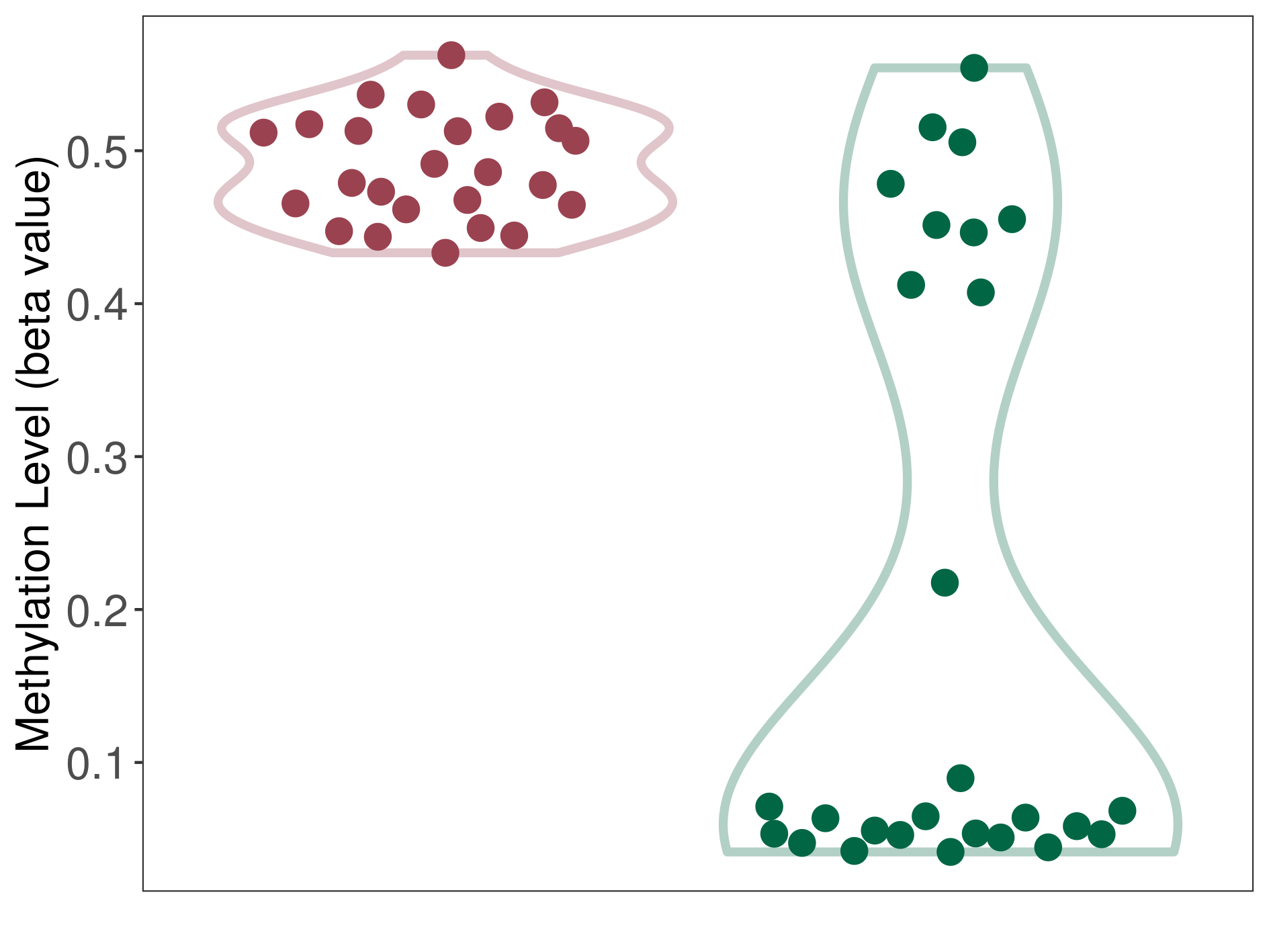
| DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) | Postviral fatigue syndrome | Significant hypermethylation | |||
| Interaction Name | DNMT-HPRT1 interaction | ||||
| The Methylation Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | Significant hypermethylation p-value: 4.30E-08; delta-beta: 4.21E-01 | ||||
| Description | DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) is reported to significantly hyper-methylate the HPRT1 gene, which leads to a significantly decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. As a result, the interaction between DNMT and HPRT1 can significantly affect the drug-metabolizing process of Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. | ||||
|
DME methylation in the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
|||||
| Violin Diagram of DME Disease-specific Methylation Level |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram | |||
| References | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ALDH16A1 is a novel non-catalytic enzyme that may be involved in the etiology of gout via protein-protein interactions with HPRT1. Chem Biol Interact. 2013 Feb 25;202(1-3):22-31. | ||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.

