Details of Host Protein-DME Interaction (HOSPPI)
| General Information of Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME ID: DME0507) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DME Name | HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 3 (EGLN3), Homo sapiens | DME Info | |||
| UniProt ID | |||||
| EC Number | EC: 1.14.11.29 (Click to Show/Hide the Complete EC Tree) | ||||
| Lineage | Species: Homo sapiens (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage) | ||||
| Interactome | |||||
| Disease Specific Interactions between Host Protein and DME (HOSPPI) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification Healthy | |||||
| ICD-11: Healthy | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| Non-coding RNA regulation | |||||
| hsa-miR-20a-5p | Health | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-20a-5p--EGLN3 regulation | [1] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Cardiomyocytes | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-20a-5p is reported to suppress EGLN3 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of EGLN3 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 3. | ||||
| ICD Disease Classification 02 Neoplasms | |||||
| ICD-11: 2B30 Lymphoma | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 1 HOSPPI | ||||
| DNA methylation | |||||
| DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) | Lymphoma | Significant hypermethylation | |||
| Interaction Name | DNMT-EGLN3 interaction | ||||
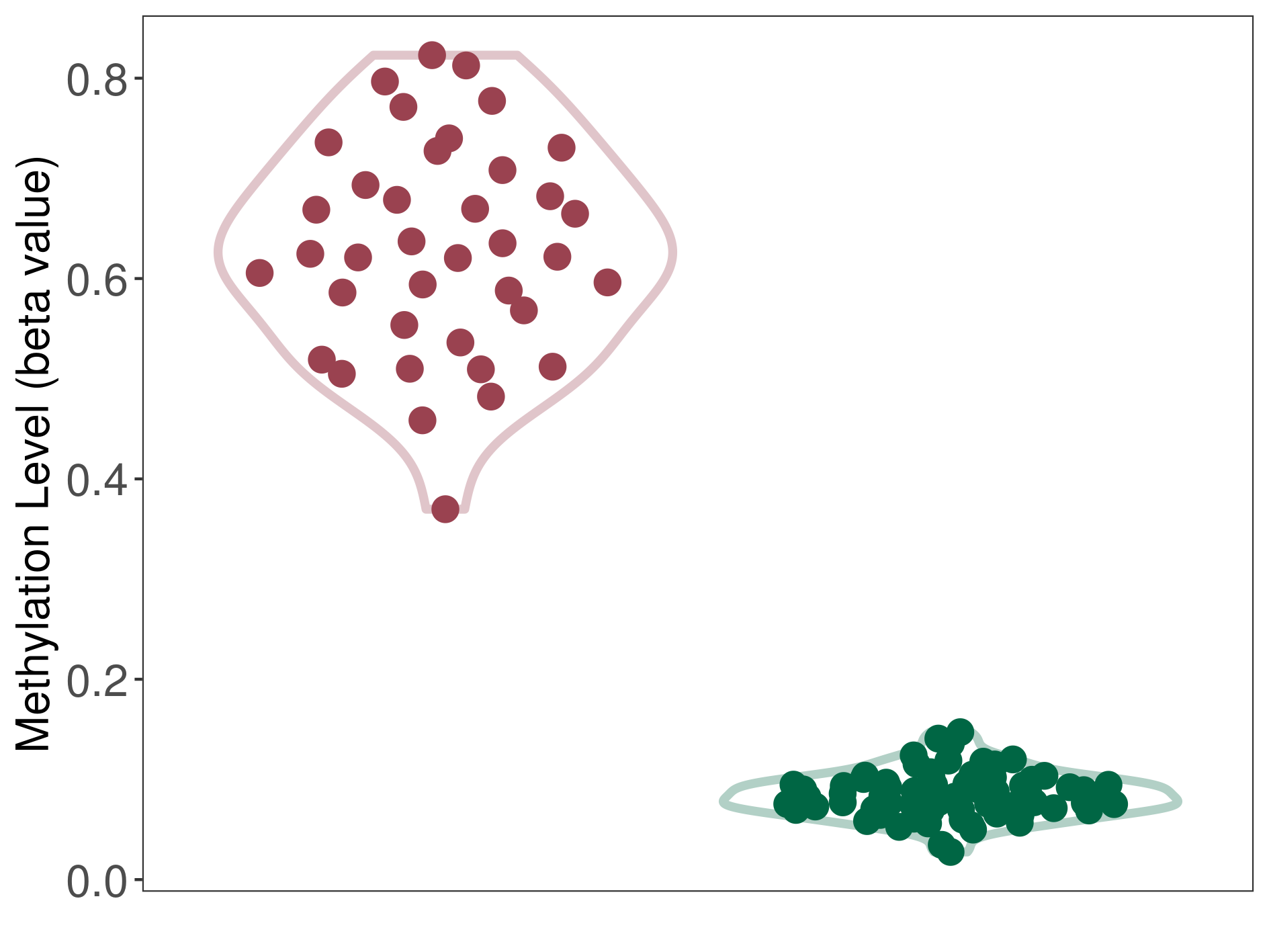
| The Methylation Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | Significant hypermethylation p-value: 3.40E-29; delta-beta: 5.40E-01 | ||||
| Description | DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) is reported to significantly hyper-methylate the EGLN3 gene, which leads to a significantly decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 3. As a result, the interaction between DNMT and EGLN3 can significantly affect the drug-metabolizing process of HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 3. | ||||
|
DME methylation in the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
|||||
| Violin Diagram of DME Disease-specific Methylation Level |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram | |||
| ICD-11: 2C12 Liver cancer | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of HOSPPI: 2 HOSPPI | ||||
| Non-coding RNA regulation | |||||
| hsa-miR-122-5p | Liver cancer | Suppression | |||
| miRBase ID | |||||
| Interaction Name | hsa-miR-122-5p--EGLN3 regulation | [2] | |||
| Studied Cell Lines | Mahlavu and SK-HEP-1 cell lines | ||||
| Description | hsa-miR-122-5p is reported to suppress EGLN3 mRNA translation by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of EGLN3 mRNA, which leads to a decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 3. | ||||
| DNA methylation | |||||
| DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) | Liver cancer | Significant hypermethylation | |||
| Interaction Name | DNMT-EGLN3 interaction | ||||
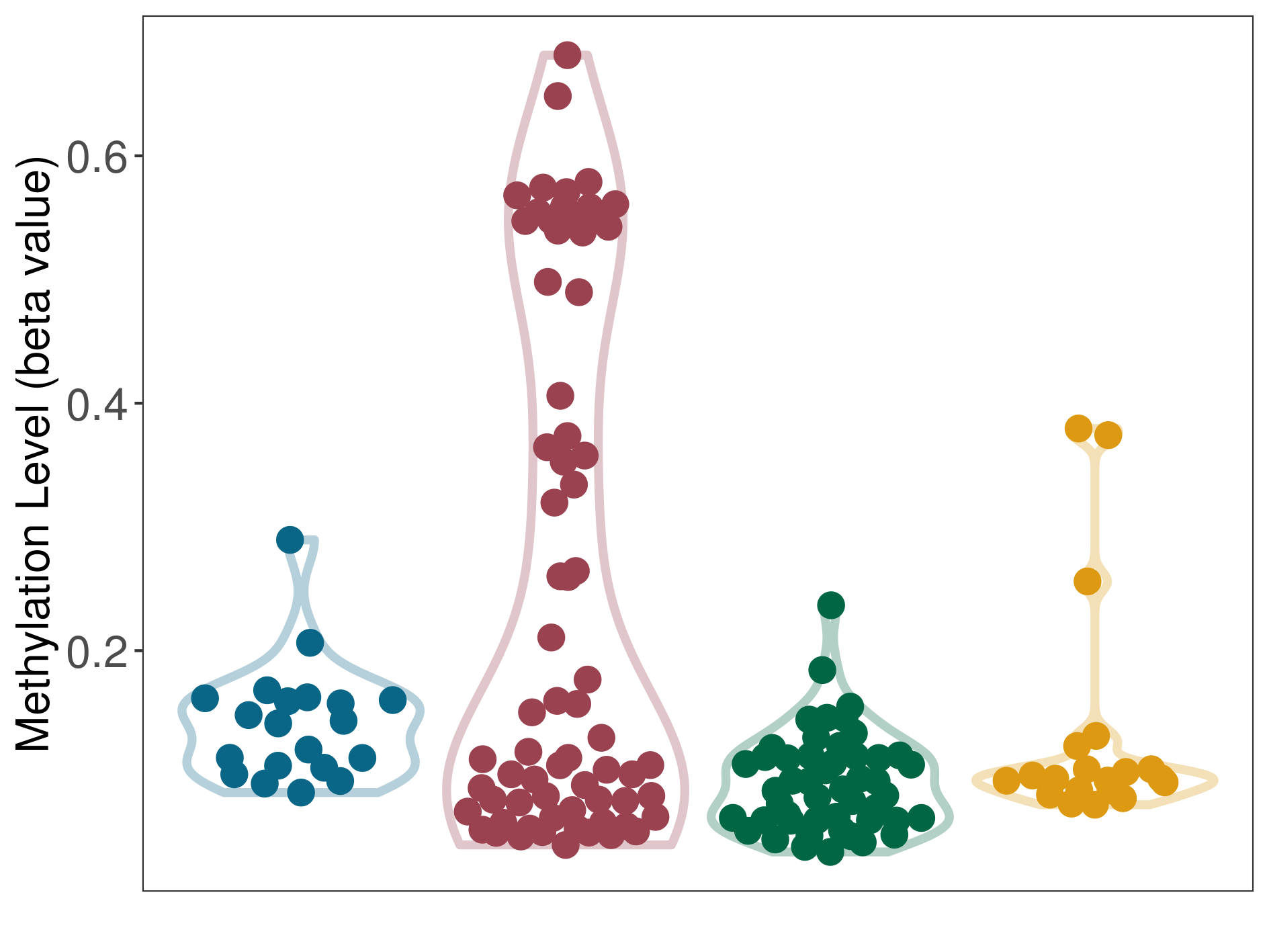
| The Methylation Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | Significant hypermethylation p-value: 3.82E-04; delta-beta: 3.29E-02 | ||||
| Description | DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) is reported to significantly hyper-methylate the EGLN3 gene, which leads to a significantly decreased expression of the drug-metabolizing enzyme HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 3. As a result, the interaction between DNMT and EGLN3 can significantly affect the drug-metabolizing process of HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 3. | ||||
|
DME methylation in the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
DME methylation in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
DME methylation in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
|||||
| Violin Diagram of DME Disease-specific Methylation Level |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram | |||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.

