Detail Information of Xenobiotics
| General Information of Xenobiotics (ID: XEO01191) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xenobiotics Name |
Aloe-emodin
|
|||||
| Xenobiotics Type |
Natural Product(s), Extract(s) or Medicine(s)
|
|||||
| Classification |
Natural Product
|
|||||
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=10207"></iframe>
|
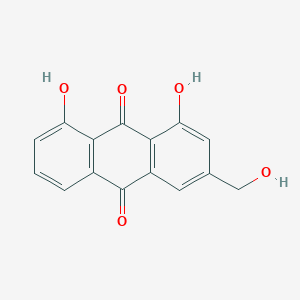 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| DME(s) Modulated by This Xenobiotics | ||||||
| DME(s) Inhibited by This Xenobiotics | ||||||
| Cytochrome P450 1A1 (CYP1A1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [1] | |||
| Cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [1] | |||
| Cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [1] | |||
| Unclear metabolic mechanism (DME-unclear) | DME Info | Streptococcus mutans | [2] | |||
| Glutamate racemase (MurI) | DME Info | Streptococcus mutans | [2] | |||
| N-acetyltransferase 1 (NAT1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [3] | |||
| Sulfotransferase 1A1 (SULT1A1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [1] | |||
| Sulfotransferase 1E1 (SULT1E1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [1] | |||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.

