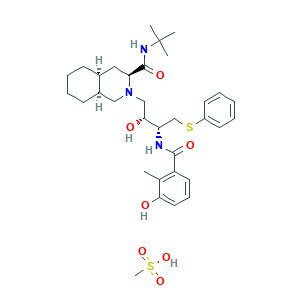
| Synonyms |
Nelfin; Nelfinavir (Mesylate); Nelfinavir Mesylate [USAN]; Nelfinavir Methanesulfonate; Nelfinavir mesilate; Nelfinavir mesylate; Nelfinavir mesylate hydrate; Nelfinavir; NELFINAVIR MESYLATE AG1343; Nelfinavir [INN:BAN]; (3S-(2(2S*,3S*),3alpha,4abeta,8abeta))-N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)decahydro-2-(2-hydroxy-3-((3-hydroxy-2-methylbenzoyl)amino)-4-(phenylthio)butyl)-3-isoquinolinecarboxamide; 159989-64-7; 1UN; 2-[2-HYDROXY-3-(3-HYDROXY-2-METHYL-BENZOYLAMINO)-4-PHENYL SULFANYL-BUTYL]-DECAHYDRO-ISOQUINOLINE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID TERT-BUTYLAMIDE; C32H45N3O4S; CHEBI:7496; HO3OGH5D7I; NLF; UNII-HO3OGH5D7I; 98D603VP8V; C32H45N3O4S.CH4O3S; CHEBI:7497; CHEMBL1205; DSSTox_CID_10777; DSSTox_GSID_33736; DSSTox_RID_79093; HSDB 7159; MFCD00931436; Nelfinavir methanesulfonate hydrate; UNII-98D603VP8V
|
| Cross-matching ID |
- PubChem CID
- 64142
- ChEBI ID
-
- CAS Number
-
- Formula
- C33H49N3O7S2
- Canonical SMILES
- CC1=C(C=CC=C1O)C(=O)NC(CSC2=CC=CC=C2)C(CN3CC4CCCCC4CC3C(=O)NC(C)(C)C)O.CS(=O)(=O)O
- InChI
- 1S/C32H45N3O4S.CH4O3S/c1-21-25(15-10-16-28(21)36)30(38)33-26(20-40-24-13-6-5-7-14-24)29(37)19-35-18-23-12-9-8-11-22(23)17-27(35)31(39)34-32(2,3)4;1-5(2,3)4/h5-7,10,13-16,22-23,26-27,29,36-37H,8-9,11-12,17-20H2,1-4H3,(H,33,38)(H,34,39);1H3,(H,2,3,4)/t22-,23+,26-,27-,29+;/m0./s1
- InChIKey
- NQHXCOAXSHGTIA-SKXNDZRYSA-N
|