Detail Information of Xenobiotics
| General Information of Xenobiotics (ID: XEO01492) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xenobiotics Name |
Trichostatin A
|
|||||
| Xenobiotics Type |
Pharmaceutical Agent(s)
|
|||||
| Classification |
Drug in Phase 1 Clinical Trial
|
|||||
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=444732"></iframe>
|
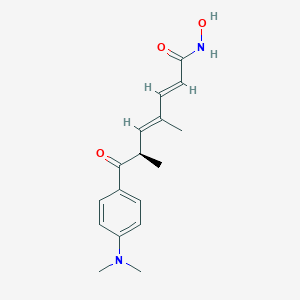 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| DME(s) Modulated by This Xenobiotics | ||||||
| DME(s) Inhibited by This Xenobiotics | ||||||
| Porphobilinogen synthase (ALAD) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [1] | |||
| Aldehyde oxidase (AOX1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [2] | |||
| Histamine N-methyltransferase (HNMT) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [3] | |||
| Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 1 (HSD17B1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [4] | |||
| Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [5] | |||
| Nitric oxide synthase inducible (NOS2) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [6] | |||
| Phosphodiesterase 7B (PDE7B) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [7] | |||
| Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 (COX-2) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [3] | |||
| Thymidylate synthase (TYMS) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [6], [8] | |||
| DME(s) Induced by This Xenobiotics | ||||||
| Aldo-keto reductase 1C1 (AKR1C1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [6] | |||
| Aldo-keto reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [9] | |||
| Butyrylcholine esterase (BCHE) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [10] | |||
| Microsomal cytochrome MCB5 (CYB5A) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [4] | |||
| Cytochrome P450 1A1 (CYP1A1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [10] | |||
| Cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [8] | |||
| Retinoic acid 4-hydroxylase 26A1 (CYP26A1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [11], [12] | |||
| Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP4) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [6] | |||
| Dihydrothymine dehydrogenase (DPYD) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [3], [13] | |||
| Hexosephosphate aminotransferase 2 (GFPT2) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [3] | |||
| L-glutamine amidohydrolase (GLS) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [6] | |||
| Glutathione S-transferase omega-1 (GSTO1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [14] | |||
| Iduronate 2-sulfatase (IDS) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [15] | |||
| Monoamine oxidase type A (MAO-A) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [6], [10] | |||
| Microsomal glutathione S-transferase 2 (MGST2) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [16] | |||
| Neprilysin (MME) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [17] | |||
| N-acetyltransferase 2 (NAT2) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [8] | |||
| Ecto-5'-nucleotidase (NT5E) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [8] | |||
| Cytosolic phospholipase A2 (PLA2G4A) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [18] | |||
| Prostaglandin reductase 1 (PTGR1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [4] | |||
| Sulfotransferase 1A1 (SULT1A1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [6] | |||
| Transglutaminase H (TGM2) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [3] | |||
| UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) | DME Info | Homo sapiens | [8] | |||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.

