Details of the Drug Metabolized by Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME)
| General Information of Drug (ID: DR0871) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug Name |
Indinavir sulfate
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Indinavir [USAN:INN:BAN]; Indinavir [USAN]; Crixivan (TN); INDINAVIR SULPHATE; Indinavir (sulfate); Indinavir Sulfate [USAN]; Indinavir sulfate; Indinavir sulfate (USAN); L 735524; MK 639; (alphaR,gammaS,2S)-alpha-Benzyl-2-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-gamma-hydroxy-N-((1S,2R)-2-hydroxy-1-indanyl)-4-(3-pyridylmethyl)-1-piperazinevaleramide sulfate (1:1) (salt); 157810-81-6; 771H53976Q; CHEBI:5899; DRG-0233; DSSTox_CID_24221; DSSTox_GSID_44221; DSSTox_RID_80126; HSDB 7158; IDV; UNII-771H53976Q; L-735524; indinavir; (1(1S,2R),5(S))-2,3,5-Trideoxy-N-(2,3-dihydro-2-hydroxy-1H-inden-1-yl)-5-(2-(((1,1-dimethylethyl)amino)carbonyl)-4-(3-pyridinylmethyl)-1-piperazinyl)-2-(phenylmethyl)-D-erythro-Pentonamide; 150378-17-9; 9MG78X43ZT; C36H47N5O4; Compound J; CHEBI:44032; N-[2(R)-HYDROXY-1(S)-INDANYL]-5-[(2(S)-TERTIARY BUTYLAMINOCARBONYL)-4(3-PYRIDYLMETHYL)PIPERAZINO]-4(S)-HYDROXY-2(R)-PHENYLMETHYLPENTANAMIDE; UNII-9MG78X43ZT
|
|||||
| Indication | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD11: 1C60] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Structure |
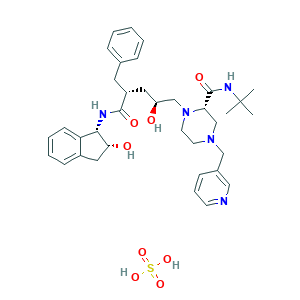 |
|||||
| 3D MOL is unavailable | 2D MOL | |||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 711.9 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 201 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 50 | Rotatable Bond Count | 12 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 6 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 | |||
| Cross-matching ID |
|
|||||
| The Metabolic Roadmap of This Drug | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Full List of Drug Metabolites (DM) of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme(s) (DME) Metabolizing This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Indinavir Sulfate was approved by FDA. The 2020 official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | |||||
| 2 | Inhibition of desipramine hydroxylation (Cytochrome P450-2D6) in vitro by quinidine and by viral protease inhibitors: relation to drug interactions in vivo. J Pharm Sci. 1998 Oct;87(10):1184-9. | |||||
| 3 | Substrates, inducers, inhibitors and structure-activity relationships of human Cytochrome P450 2C9 and implications in drug development. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(27):3480-675. | |||||
| 4 | Enzymes in addition to CYP3A4 and 3A5 mediate N-demethylation of dextromethorphan in human liver microsomes. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1999 Oct;20(7):341-6. | |||||
| 5 | Differential inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A4, 3A5 and 3A7 by five human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease inhibitors in vitro. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2006 Jan;98(1):79-85. | |||||
| 6 | Inhibition of bilirubin metabolism induces moderate hyperbilirubinemia and attenuates ANG II-dependent hypertension in mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009 Sep;297(3):R738-43. | |||||
| 7 | Hepatic and intestinal metabolism of indinavir, an HIV protease inhibitor, in rat and human microsomes. Major role of CYP3A. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997 Apr 25;53(8):1187-95. | |||||
| 8 | Involvement of CYP3A4 and MDR1 in altered metabolism and transport of indinavir in 1,25(OH)(2)D(3)-treated Caco-2 cells. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2023 Apr 1;183:106396. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2023.106396. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.

